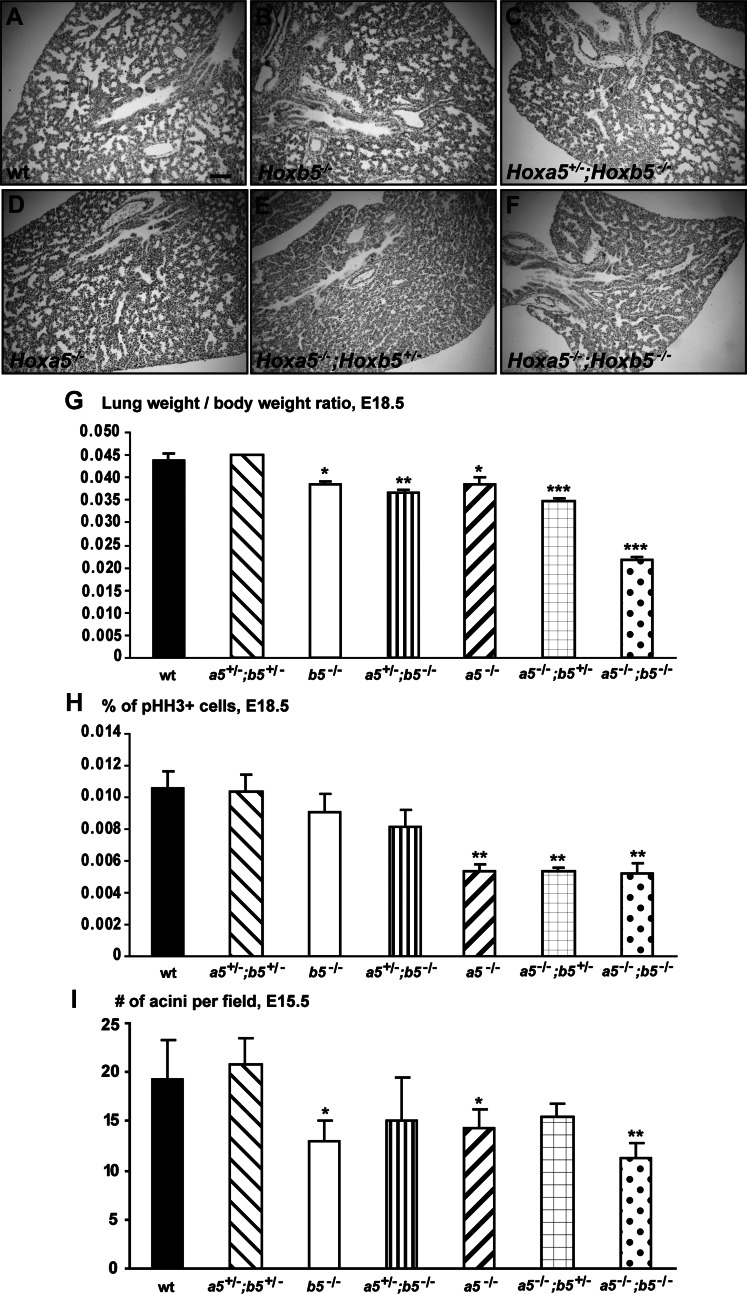
Fig. 2.
Comparative analyses of lungs from Hoxa5;Hoxb5 mutant embryos. A–F: comparative lung histology of E18.5 Hoxa5;Hoxb5 embryos. WT, Hoxb5−/−, and Hoxa5+/−;Hoxb5−/− specimens presented a normal lung structure with dilated peripheral saccules and thin mesenchyme, whereas lungs from Hoxa5−/− embryos exhibited narrower air spaces and thicker mesenchyme. The phenotype worsened with the number of Hoxb5 mutant alleles, and lungs from Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5−/− embryos were smallest. Scale bar: 100 μm. G: at E18.5, the lung weight-to-body weight ratio was statistically lower for Hoxa5−/−, Hoxb5−/−, Hoxa5+/−;Hoxb5−/−, Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5+/−, and Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5−/− embryos compared with WT. H: lung hypoplasia in E18.5 Hoxa5−/−, Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5+/− and Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5−/− embryos correlated with a statistically reduced proliferation in the lung. I: lung branching at E15.5, as estimated by the number of acini per field, was statistically less extensive in Hoxa5−/−, Hoxb5−/− and Hoxa5−/−;Hoxb5−/− embryos compared with WT. Values are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.