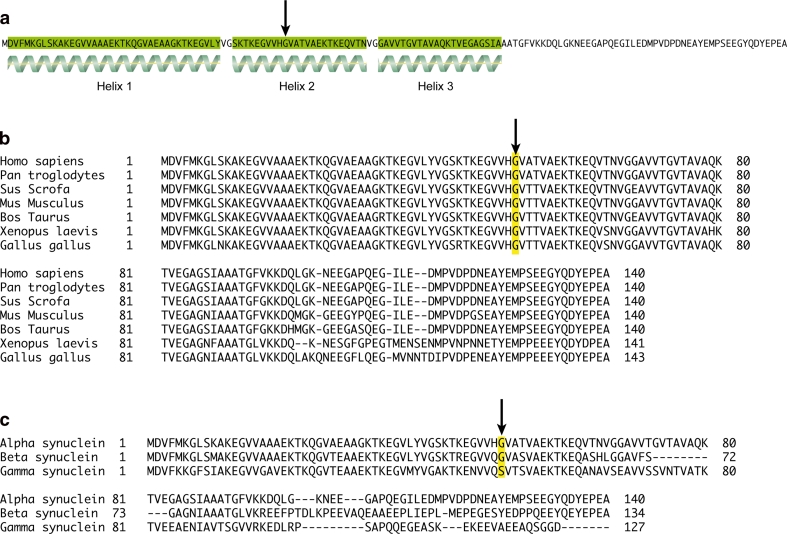
Fig. 2.
α-Synuclein protein structure and conservation as shown by amino acid sequence alignment. Amino acid sequence of human α-synuclein, showing regions of secondary structure (alpha helices highlighted in green). The G51 residue is indicated by an arrow, and sits in the middle of helix 2 (a). Sequence alignment of α-synuclein amino acid sequences from Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Sus scrofa, Mus musculus, Bos taurus, Xenopus laevis and Gallus gallus. The G51 residue highlighted in yellow and indicated by an arrow is conserved throughout these organisms (b). Sequence alignment of human α-, β- and γ-synuclein amino acid sequences, with the G51 residue is highlighted in yellow and indicated by an arrow (c). This residue is conserved in α- and β-synuclein, but is replaced by a serine residue in γ-synuclein