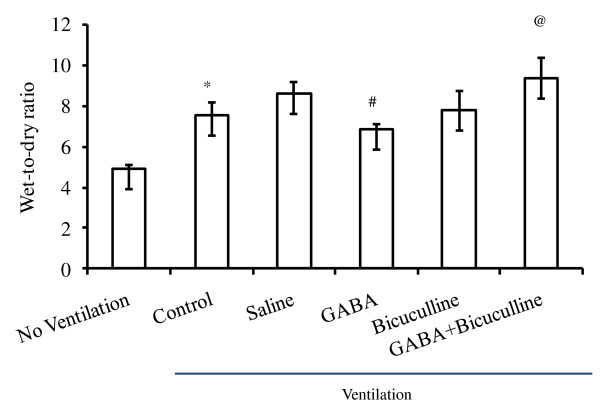
Figure 1.
Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-receptor modulators on ventilator-induced pulmonary edema. Adult female rats were subjected to a high tidal volume (40 ml/kg BW) ventilation for 60 minutes with and without instillation of GABA (500 μM) and bicuculline (200 μM). The control lungs were instilled with saline. At the end of ventilation, lungs were analyzed for edema formation by measuring the wet-to-dry ratio. Data shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 4 to 6 per group). *P < 0.05 versus nonventilated animals; #P < 0.05 versus saline; and @P < 0.05 versus GABA.