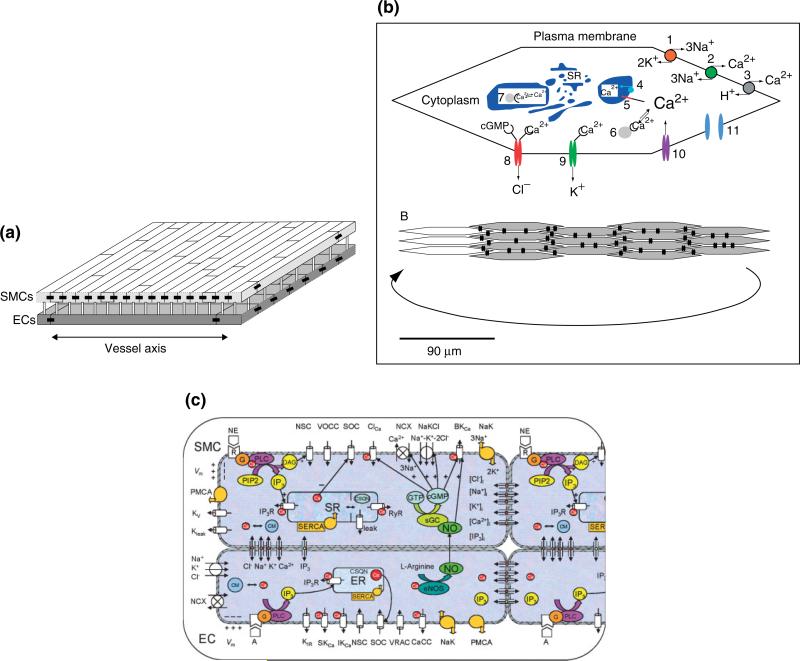
FIGURE 3.
Multicellular models of the vascular wall. (a) The Koenigsberger model integrates on a two-dimensional grid model equations for SMCs superposed on a two-dimensional grid of ECs. ECs are arranged parallel and SMCs perpendicular to the vessel axis (reproduced with permission from Ref 73. Copyright 2005 Elsevier). Cell geometry is approximated by a rectangle. Each cell is connected with its nearest neighbors on the same layer (homocellular connection) and with the cells on the other layer directly superposed on it (hetero-cellular connection). (b) A model of the SMC layer introduced by Jacobsen and coworkers (Reproduced with permission from Ref 76. Copyright 2007 American Physiological Society). Each SMC (upper panel) contains: Na+/K+-ATPase (1), NCX (2), plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (3), sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (4), SR calcium release channel (5), cytoplasmic calcium buffer (6), SR calcium buffer (7), cGMP-sensitive calcium-dependent chloride channel (8), calcium-activated potassium channels (9), voltage-sensitive calcium channel (L-type calcium channel; 10), and gap junction (11). The SMCs are arranged into a single-layered cell plate (lower panel). Each spindle-shaped cell couples to neighboring cells through gap junctions (black double-barrel structures). (c) Multicellular model of a vessel segment presented by Kapela and coworkers.78,79 ECs and SMCs are placed in appropriate arrangement. Cells are coupled by nitric oxide (NO) and myoendothelial gap junctions permeable to Ca2+, Na+, K+, and Cl– ions, and IP3. Kir—inward rectifier K+ channel; VRAC—volume-regulated anion channel; SKCa, IKCa and BKCa—small-, intermediate-, and large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels; SOC—store-operated channel; NSC—nonselective cation channel, CaCC and ClCa—Ca2+-activated chloride channel; NaK—Na+-K+-ATPase; PMCA—plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase; NCX—Na+/Ca2+ exchanger; NaKCl—Na+-K+-Cl– cotransport; Kv—voltage-dependent K+ channel; Kleak—unspecified K+ leak current; VOCC—voltage-operated Ca2+ channels; SR/ER—sarco/endoplasmic reticulum; IP3R—IP3 receptor; RyR—ryanodine receptor; SERCA—SR/ER Ca2+-ATPase; CSQN—calsequestrin; CM—calmodulin; R—receptor; G—G-protein; DAG—diacylglycerol; PLC—phospholipase C; sGC—soluble guanylate cyclase; cGMP—cyclic guanosine monophosphate.