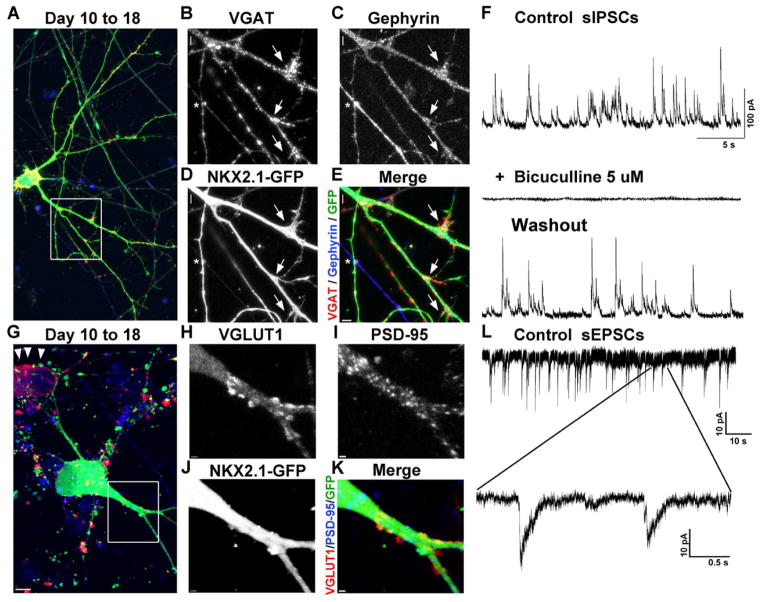
Figure 5. NKX2.1::GFP+ GABAergic interneurons receive both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs.
A–E) Collapsed z-stack confocal image showing NKX2.1::GFP+, vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT; red in A), and the post-synaptic GABAergic marker gephyrin (blue in A). The dendrites of this GFP+ cell that co-label with gephyrin are receiving VGAT-expressing pre-synaptic terminals (arrows). In addition, a GFP+ axonal process formed a VGAT+ pre-synaptic terminal adjacent to a GFP negative, gephyrin-expressing post-synaptic process (asterisk). F) Whole-cell patch clamp reveals spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) recorded from an NKX2.1::GFP+ neuron (SHH 10 to 18 protocol), which are reversibly blocked by the addition of the GABA-A receptor antagonist bicuculline. G-K) Collapsed z-stack confocal image showing NKX2.1::GFP, vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (VGLUT1; red in G), and the post-synaptic marker PSD-95 (blue; C). This GFP+ cell has dendrites that co-label with PSD-95 that are adjacent to VGLUT1-expressing pre-synaptic terminals. Note the presence of a GFP negative cell expressing VGLUT1 (red; G arrowheads), confirming the presence of excitatory glutamatergic neurons in the culture. L) Consistent with the apparent presence of glutamatergic synaptic inputs, spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) were detected in the NKX2.1::GFP+ neurons (10 to 18). All cells were plated on mouse cortical feeder following FACS for NKX2.1::GFP at day 32. See also Figure S4.