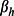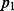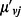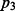|
Biting rate (number of bites taken per vector per day) |
0.2–0.5 days−1
|
Parameter varied to assume vectors bite on average once every 2 to 5 days |
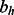
|
Birth rate of humans |
1/18,250 days−1
|
Equal to host death rate to ensure constant population size |
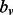
|
Birth rate of vectors |
1/10 days−1 days−1
|
Equal to vector death rate to ensure constant population size |
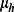
|
Death rate of humans |
1/18,250days−1
|
Assumes host average life expectancy of 50 years |

|
Death rate of worms |
13/37500 days−1
|
[39]
|
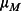
|
Death rate of microfilariae |
1/300 days−1
|
[39]
|
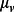
|
Death rate of vectors |
0.1 days−1
|
Approximate mortality at 25°C [56]
|

|
Probability of infectious vectors transferring infection to susceptible hosts |
1/25 |
[57]
|
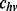
|
Probability of infectious hosts transferring infection to susceptible vectors |
9/100 |
[57]
|

|
Production rate of mf per worm |
1/15 days−1
|
[39]
|

|
Rate of development from immature to L3 larvae |
0.08 days−1
|
Development rate of [58] evaluated at 25°C |
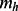
|
Rate at which infected hosts become infectious |
1/10 days−1
|
[57]
|
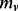
|
Rate at which infected vectors become infectious |
0.02 days−1
|
Evaluation of  at T = 25°C (where at T = 25°C (where 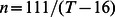 for P. falciparum) [34] for P. falciparum) [34]
|
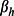
|
Rate at which humans return to susceptible from recovered |
1/7 days−1
|
Host population assumed to experience loss of immunity within 1 week |
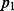
|
Proportion of L3 leaving mosquitoes per bite |
0.414 |
[39]
|

|
Proportion of L3 leaving mosquitoes that enter host |
0.0003 |
[39], [59]
|

|
Death rate of larvae |
0 days−1
|
Larval mortality assumed to arise only due to vector mortality |
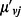
|
Additional mortality rate of larval-infected vectors with malaria status 
|
0.1 days−1
|
Uncertain parameter varied in sensitivity analysis (but within bounds to ensure realistic vector mortality at 25°C) |
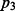
|
Probability of mf entering the vector upon biting an LF-infected host |
0.37 |
[39]
|

|
Probability of mf entering the vector developing into L3 larvae |
1 |
[39]
[25]
|

|
Force of immunity (strength of immune response) |
0.2 |
[39], [59]
|

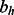
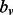
 days−1
days−1
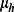

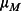
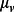

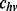


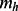
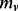
 at T = 25°C (where
at T = 25°C (where 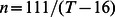 for P. falciparum) [34]
for P. falciparum) [34]