FIGURE 3:
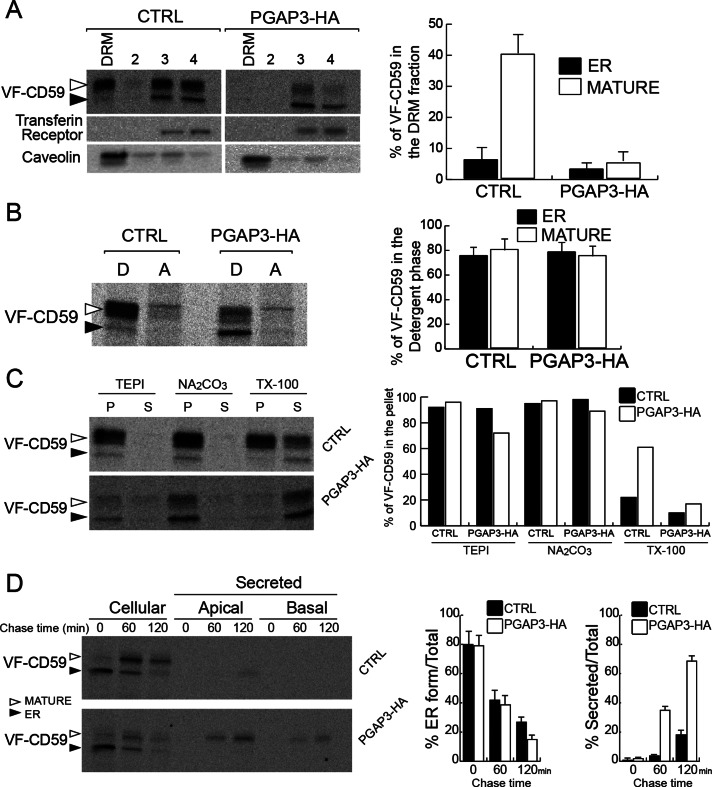
Overexpression of PGAP3-HA results in loss of GPI-APs from DRM. (A) DRM assay for VF-CD59 in control and PGAP3-HA cells and quantification of the proportion of VF-CD59 in the DRM fraction. Radiolabeled VF-CD59 was immunoprecipitated from the density gradient fractions (DRM [top], 2, 3, and 4 [bottom]). Caveolin and the transferrin receptor were revealed by Western blotting. (B) Control and PGAP3-HA cells were grown on plastic dishes, pulse labeled, and chased for 1 h. Phase partitioning of newly synthesized VF-CD59 in control and PGAP3-HA cells into the detergent phase (D) and aqueous phase (A) of a Triton X-114 solution. (C) Membrane association of newly synthesized VF-CD59 prepared as in B. After homogenization of the cells and incubation of the extracts in buffer alone (TEPI), 0.1 M Na2Co3, pH 11, and 1% (wt/vol) Triton X-100, ultracentrifugation was performed to separate the membrane fraction (P) and the soluble fraction (S). (D) Cells grown on Transwell filters for 6 d were pulse labeled and chased for various times, as indicated. The cells and the media from the upper (apical) and lower (basal) chambers were analyzed. ER-to-Golgi transport was assessed by the disappearance of the ER form (left histogram). Secretion was expressed as percentage of the sum of apically and basolaterally secreted VF-CD59 compared with the total VF-CD59 signal (right histogram). (A, B, D) The data shown are means of three independent experiments. Error bars, 1 SD from the mean. (A–D) Newly synthesized VF-CD59 was detected by immunoprecipitation and PhosphorImaging after SDS–PAGE. The black arrowheads indicate the ER form and the white arrowheads the mature form of VF-CD59.