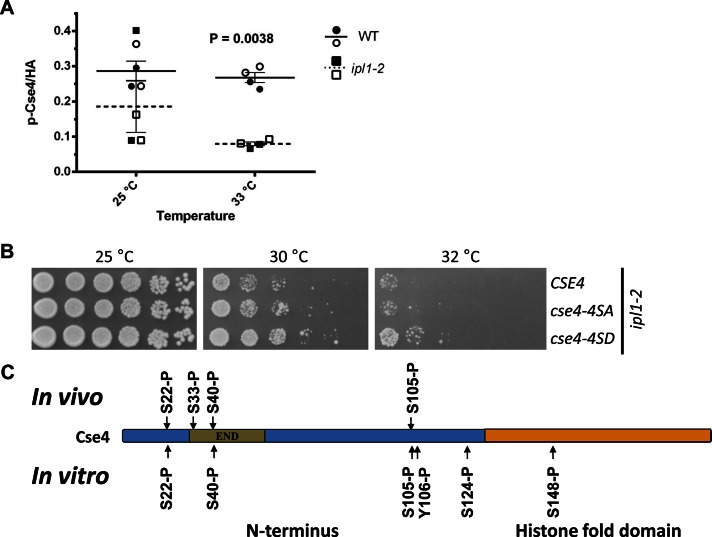
FIGURE 3:
Ipl1 phosphorylates Cse4 in vivo and in vitro and phosphomimetic cse4-4SD suppresses temperature sensitivity of an ipl1-2 strain. (A) Ipl1 contributes to the phosphorylation of centromere-associated Cse4. ChIP experiments were performed with WT (YMB8525) and ipl1-2 (YMB8528) strains grown at 25°C and shifted to 33°C for 3 h. The p-Cse4 signal is plotted, with lines showing the mean ± SE of the mean. Results from two independent experiments were pooled. Statistical significance was analyzed by two-way ANOVA (strain, temperature), which indicated that observed variation was significant and predominately due to differences between the wild-type and ipl1-2 strains (p = 0.0038). Results of pairwise tests were corrected for multiple comparisons (Bonferroni). Open symbols, CEN3; filled symbols, CEN4. (B) Phosphomimetic cse4-4SD suppresses the temperature sensitivity of an ipl1-2 strain. Serial dilutions of ipl1-2 (KT1963) with CSE4 (YMB8528), cse4-4SA (YMB8529), or cse4-4SD (YMB8530) were plated on YPD medium and incubated at the indicated temperatures for 2–3 d. (C) Ipl1 phosphorylates Cse4 in vitro. Products of in vitro kinase assays using purified Cse4, ATP, and Ipl1-Sli15 at 30°C for 90 min were analyzed by mass spectrometry. Cse4 modification sites are shown, along with those identified by in vivo analysis (Figure 1A; also see Tables 1 and 2 and Supplemental Figure 3B).