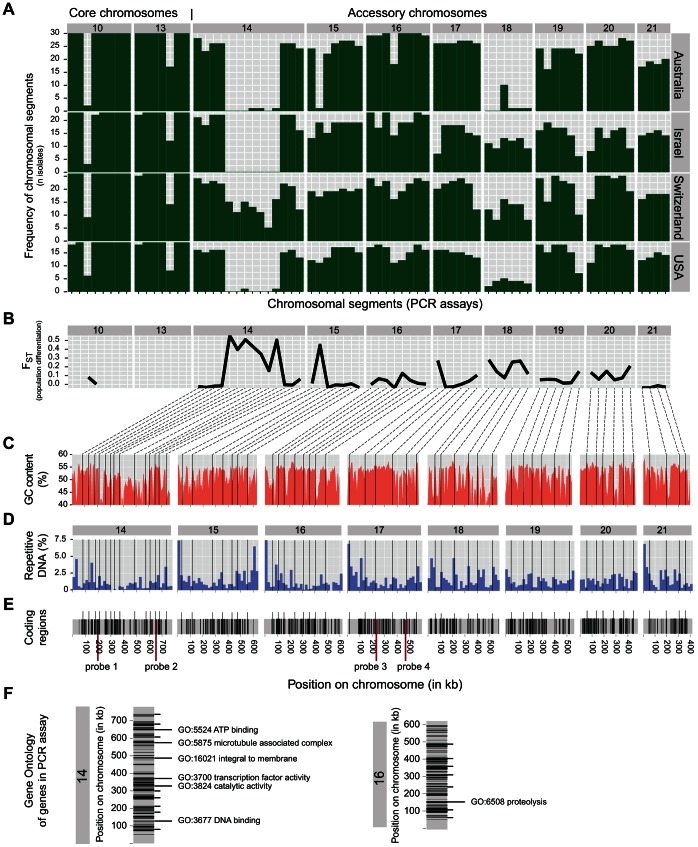
Figure 1. Global survey of diversity in accessory chromosomes of Zymoseptoria tritici.
A) Presence or absence of chromosomal segments assayed by PCR in a global collection of four field populations located in Australia, Israel, United States and Switzerland (total n = 98). Green bars represent the number of chromosomal segments found within the populations. Core chromosomes 10 and 13 were included for comparison with the accessory chromosomes 14–21. B) Population differentiation based on the presence of chromosomal segments calculated by Wright's FST. C) The physical location of each gene used for the PCR assays is shown on schematics drawn for each accessory chromosome. The variation of GC-content along the chromosomes is shown in red. D) Content of short direct repeats assessed in 20 kb segments. E) Location of coding regions according to the reference genome [46]. The location of probes used for Southern hybridizations to CHEF gels are indicated in red. F) Gene ontology terms for genes comprised in the PCR assay. Only genes on accessory chromosomes 14 and 16 were described by gene ontology terms [46].