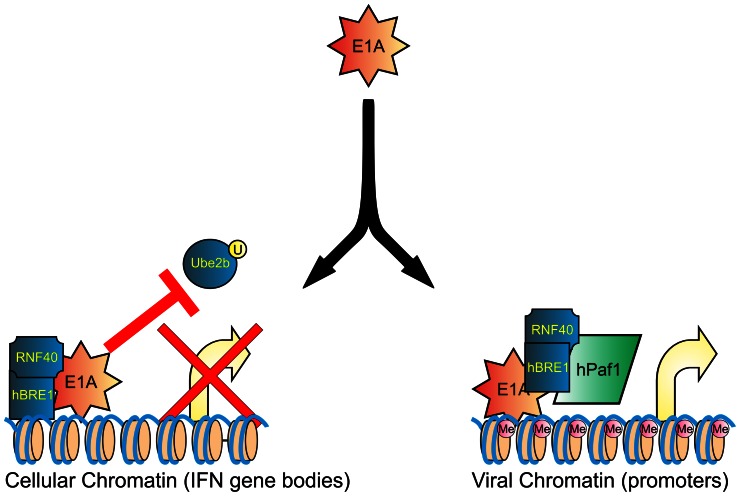
Figure 8. The interaction of E1A with hBre1 serves two completely different purposes during HAdV infection.
By disassociating the catalytically active Ube2b component from the hBre1 complex, E1A inhibits H2B monoubiquitination and suppresses transcription of IFN responsive genes (left panel). However, E1A then retasks the catalytically inactive hBre1 complex by using it as a scaffold to recruit hPaf1, leading to localized H3K4 and H3K79 trimethylation and stimulation of viral gene expression.