Table 2.
PA63 conductance block and cytotoxicity inhibition by cationic cyclodextrins
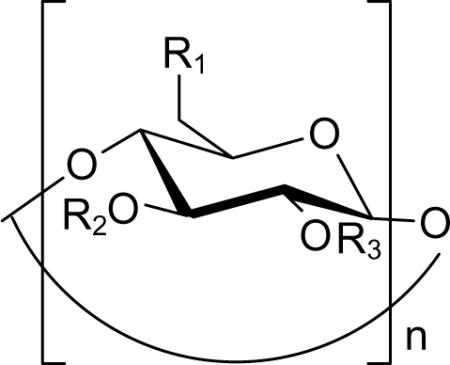
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | n | R1 | R2, R3 | Inhibition of conductance IC50, nM | Inhibition of cytotoxicity IC50, μM |
| I. Hepta-6-aminoalkyl β-cyclodextrin derivatives 52 | |||||
| 1 | 7 | -NH2 | -H | 140 ± 90 | 20 ± 9 |
| 2 | 7 | -S(CH2)2NH2 | -H | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 7.8 ± 2.4 |
| 3 | 7 | -S(CH2)3NH2 | -H | 0.57 ± 0.39 | 2.9 ± 1.0 |
| 4 | 7 | -S(CH2)4NH2 | -H | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± .2.4 |
| 5 | 7 | -S(CH2)5NH2 | -H | 3.8 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 2.4 |
| 7 | 7 | -S(CH2)6NH2 | -H | 0.97 ± 0.38 | 0.6 ± 0.3 |
| 8 | 7 | -S(CH2)7NH2 | -H | 4.6 ± 3.2 | 1.9 ± 1.1 |
| 9 | 7 | -S(CH2)8NH2 | -H | 2.4 ± 0.95 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 10 | 7 | -S(CH2)10NH2 | -H | 27.0 ± 17.0 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| II. Hepta-6-guanidinealkyl β-cyclodextrin derivatives 52 | |||||
| 11 | 7 |
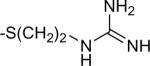
|
-H | 5.3±3.2 | 8.9±6.0 |
| 12 | 7 |
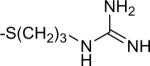
|
-H | 12.6±9.0 | 12.2±2.9 |
| III. Hepta-6-arylamine β-cyclodextrin derivative 52,62 | |||||
| 13 | 7 |
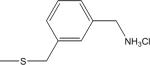
|
-H | 0.13±0.10 | 0.8±0.5 |
| IV. Cationic α- and γ cyclodextrin derivatives 62 | |||||
| 14 | 6 | -NH2 | -H | 1200 ± 300 | >100 |
| 15 | 8 | -NH2 | -H | 170 ± 50 | 12 ± 3 |
| 16 | 6 |
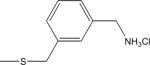
|
-H | 29±5 | 45±13 |
| 17 | 8 |
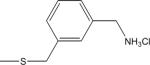
|
-H | 2.8±1.3 | 5.4±0.8 |
| V. Novel β-cydodextrin derivatives 60 | |||||
| 18 | 7 |
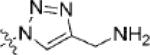
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 19 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 20 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 21 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 22 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 23 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 24 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | 26 ± 21 |
| 25 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | 3.2 ± 1.9 |
| 26 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | 20 ± 14 |
| 27 | 7 |
|
-H | n/a | >100 |
| 28 | 7 | -H |
|
n/a | 4.1 ± 0.4 |
| 29 | 7 | -H |
|
n/a | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| VI. α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrin derivatives tested against α-hemolysin 62 | |||||
| 30 | 6 |
|
-H | >5000 | >100 |
| 31 | 7 |
|
-H | ~50 | 3.3±2.3 |
| 32 | 8 |
|
-H | >5000 | >100 |
