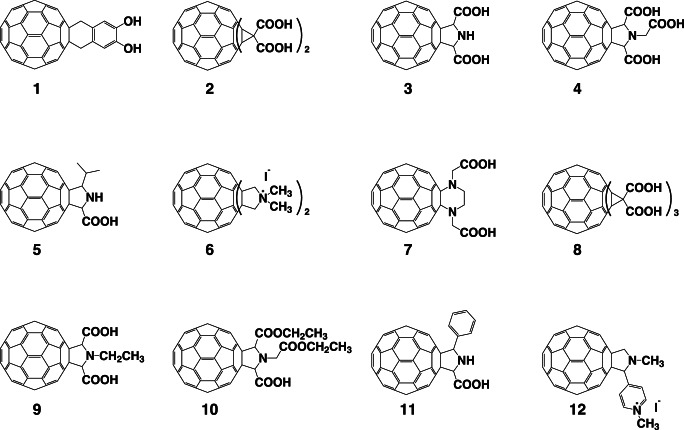
Figure 1. Chemical structures of the C60 fullerene derivatives tested in this study.
The chemical structures of the fullerene derivatives examined in this study are shown. The sources for these structures are described in the Materials and Methods. No. 1, 1,4-dihydro-6,7-dihydroxy [60]fullerenonaphthlene; no. 2, [60]fullerenodicyclopropane-1,1,1′,1′-tetracarboxylic acid; no. 3: [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid; no. 4, 1-carboxymethyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid; no. 5, 5-isopropyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; no. 6∶1,1,1′,1′-tetramethyl [60]fullerenodipyrrolidinium diiodide; no. 7, [60]fullerenopiperazine-1,4-diacetic acid; no. 8: [60]fullerenotricyclopropane-1,1,1′,1′,1′′,1′′-hexacarboxylic acid; no. 9, 1-ethyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid; no. 10, 1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid 2-ethyl ester; no. 11, 5-phenyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; and no. 12, 4-(1′-methyl [60]fullerenopyrrolidin-2′-yl)-1-methylpyridinium iodide.