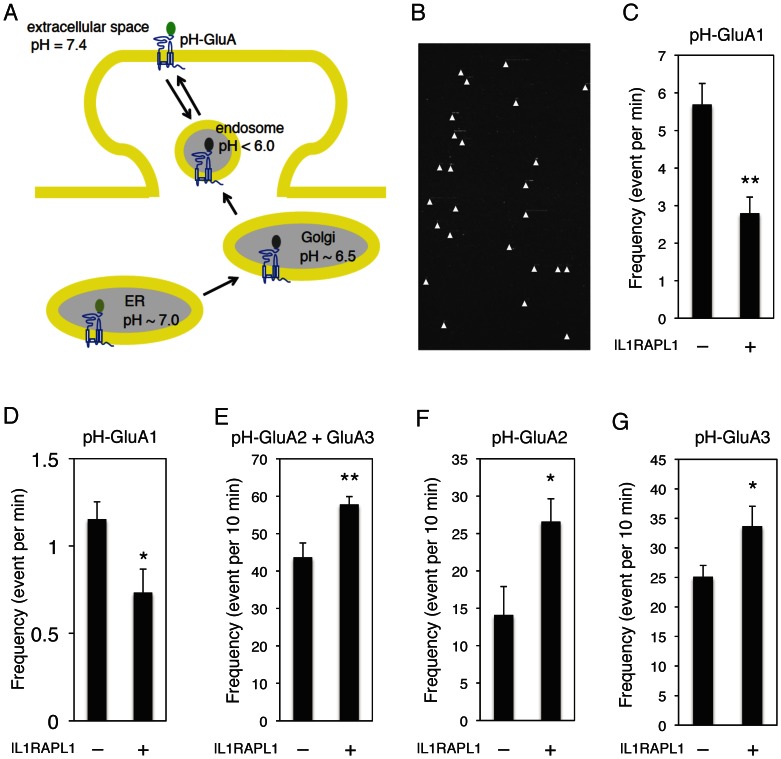
Figure 7. IL1RAPL1 regulates AMPA receptor newly insertion to surface in cortical neurons.
A, pHluorin fluorescence of pH-GluA in neurons. pHluorin signals are invisible in Golgi and endosome (in low pH) and weakly visible in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER, pH ∼7.0). Bright punctate signals of fluorescence increase when pH-GluA is inserted to surface and the pHluorin tag is exposed to the extracellular space (pH 7.4). B, Representative real time visualization of typical pH-GluA1 insertion events. Signal position around a neuron (y-axis, 83 μm) and time (x-axis, 5 min). Each ‘comet-like’ event is indicated by a white arrowhead. The sudden rising and disappear in fluorescence represents individual surface expression of pH-GluA1. C, E–G, Effects of IL1RAPL1 overexpression on the insertion frequency of pH-GluA1 (n = 9, n = 7) (C), pH-GluA2/GluA3 (n = 10, respectively) (E), pH-GluA2 (n = 10, respectively) (F) and pH-GluA3 (n = 10, respectively) (G). D, Longer observation of IL1RAPL1 effects on the pH-GluA1 insertion frequency (n = 4, respectively). Signals existing on surface over 1 min were calculated. Student t-test. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. Error bars represent s.e.m.