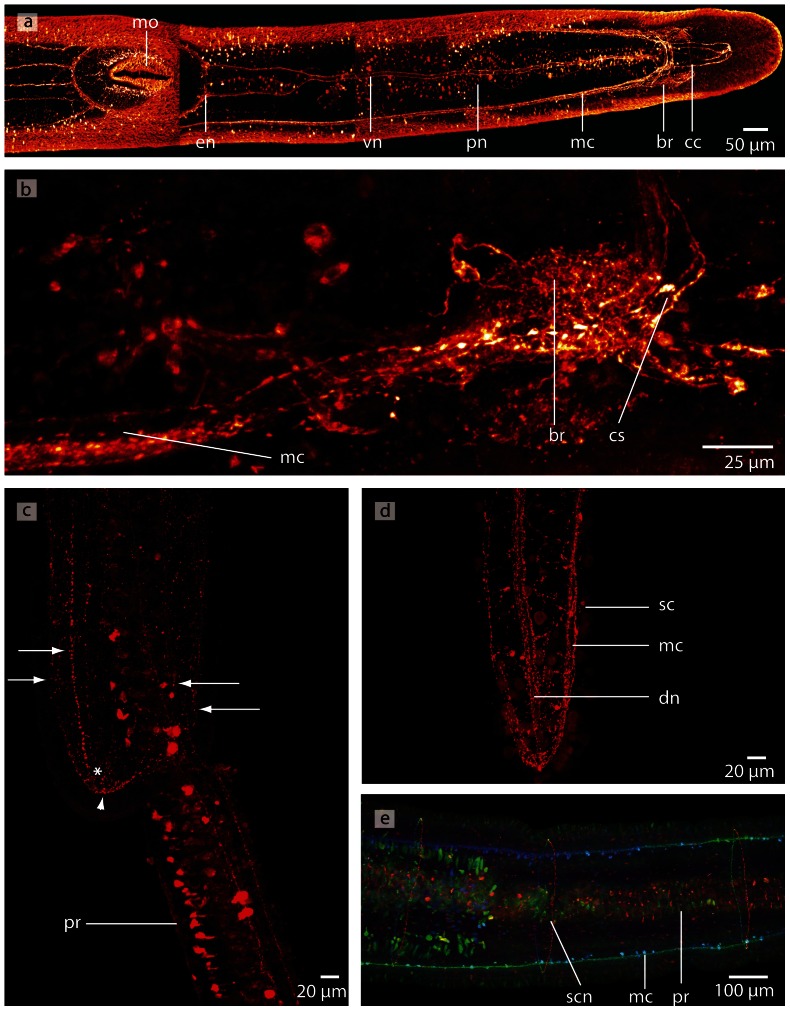
Figure 9. Procephalothrix filiformis, confocal laserscanning (cLSM) micrographs of differently immunostained whole mounts.
a: Anti-FMRF. The cephalic cords (cc) originate in the lateral aspects of the brain (br). The lateral medullary cords (mc) extend the full length of the animal. There are two proboscidial nerves (pn) that run opposed to each other, along both sides of the proboscis. The esophageal nerves (en) originate at the ventral nerve (vn) and branch shortly before the mouth opening (mo). b: Anti-FMRF. Only few neuronal cell somata (cs) of the brain (br) are immunoreactive against FMRF. c: Anti-FMRF. Four minor nerves (arrow) unite in the tip of the animals' head (arrowhead). The nerves are interconnected by a circular nerve (asterisk) d: Anti-FMRF. The dorsal nerve (dn) is connected to the medullary cords (mc) in the very posterior part of the animal; bottle shaped sensory cells (sc) are distributed all over the body. e: Anti serotonin. The medullary cords (mc) are connected by serial arranged circular nerves (scn). Note that the proboscis nerves show no immunoreactivity against serotonin. pr proboscis.