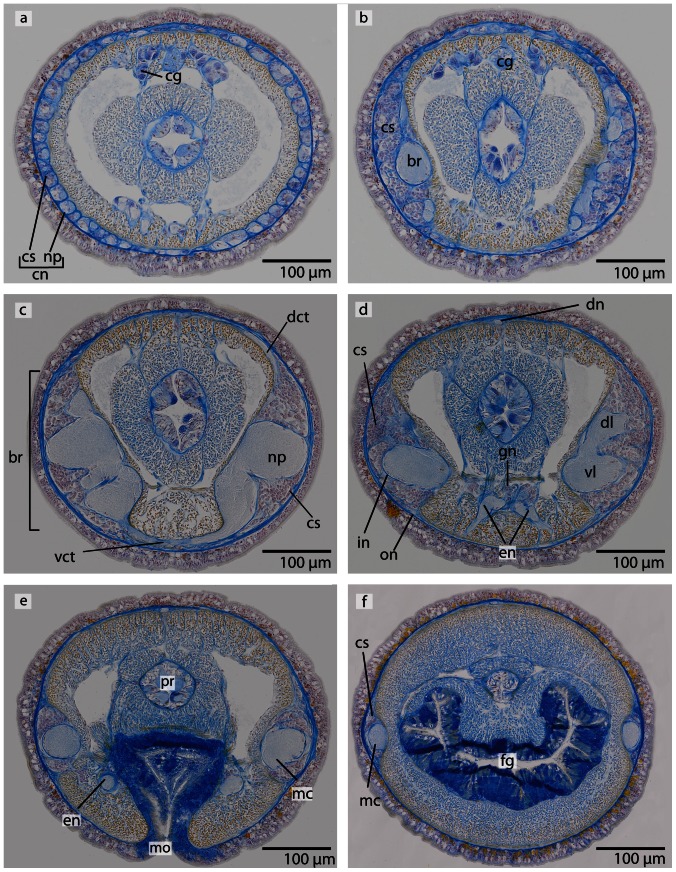
Figure 22. Callinera grandis, light micrographs of Azan stained transverse sections of the brain.
a: The cephalic nerves (cn) are composed of neuropil (np) and neuronal cell somata (cs), a cephalic gland (cg) is located dorsally. b: The anterior region of the brain (br) is covered by a enormous layer of cell somata (cs). c: The brain is composed of a central neuropil (np) and a surrounding layer of cell somata (cs). The two halves of the brain are connected by ventral (vct) and dorsal (dct) commissural tracts. d: Posteriorly the brain is divided into a ventral (vl) and dorsal (dl) section. A dorsal nerve (dn) arises from the dorsal commissural tract, and the paired esophageal nerves (en) arise from the ventral commissural tract. Shortly anterior to the foregut a concentration of neurons (gn) occurs which are associated with the esophageal nerves. The somata are separated from the neuropil by an inner neurilemma (in), and the whole brain is enclosed by an outer neurilemma (on). e: The ventral lobes of the brain are confluent with the lateral medullary cords (mc). mo: mouth opening, pr: proboscis. f: The lateral medullary cords (mc) run to the posterior of the animal. The cell somata (cs) cover the neuropil in a C-shaped manner. fg foregut.