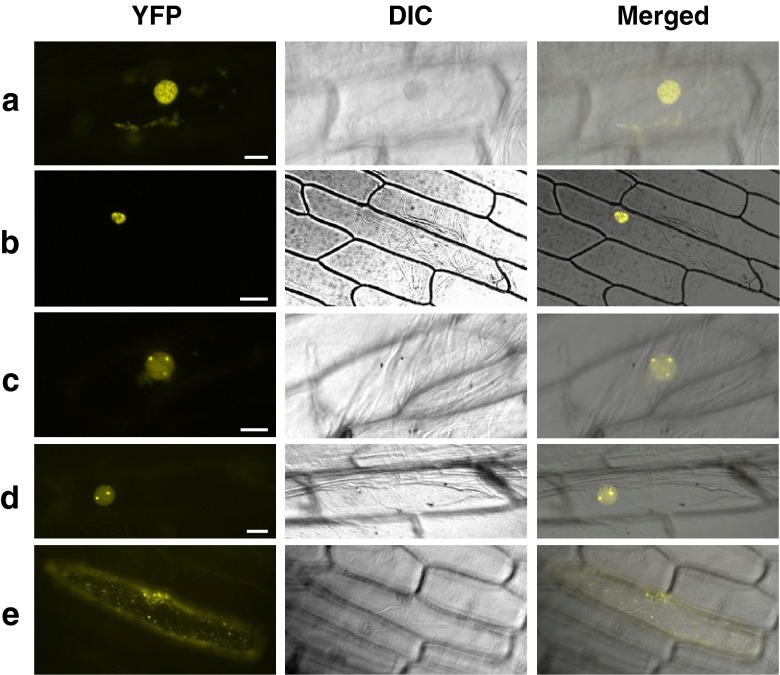
Fig. 2.
BiFC analysis of AtCSP3-interacting proteins. Representative reconstituted YFP fluorescence (left), differential interference contrast (DIC) (center) and merged (right) images of onion epidermal cells co-bombarded with nYFP-AtCSP3 and cYFP-COL15 (a), cYFP-AtPABN3 (b), cYFP-At4g10970 (c), cYFP-RPL40A/UBQ2 (d), cYFP-DCP5 (e). Reconstitution of functional YFP as detected by YFP fluorescence occurs in nuclear speckles (a and b), the nucleolus and nucleoplasm (c and d), cytoplasm (e). Bars are 50 μm (b) and 20 μm (a and c–e). BiFC assay was carried out as previously described (Shimizu et al. 2005). For vector construction, amplified AtCSP3 cDNA was cloned into pSAT4-nEYFP-N1 to fuse with the N-terminal part of YFP. Similarly, cDNAs for AtCSP3-interacting proteins (CIPs) were cloned into pSAT1-cEYFP-N1 to make a fusion with the C-terminal YFP. Primers used for plasmid construction are listed in Supplementary Table 1. For transient expression, gold particles (1.0 μm) coated with plasmid DNA (2.5 μg) were introduced into onion epidermal cells using a PDS1000/He particle gun (Bio-Rad, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Onion (Allium cepa) epidermal peels were placed on MS agar medium and used for bombardment with a rupture setting of 1,100 psi. The bombarded samples were incubated for 16 h at 22 °C and were observed by a Leica FW 4000 microscope