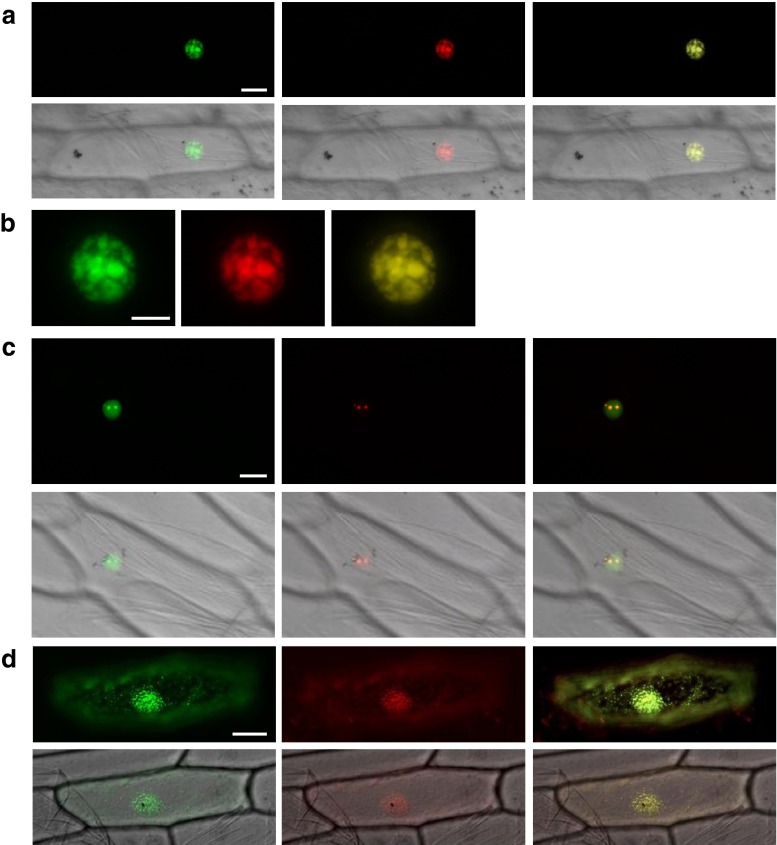
Fig. 3.
tlubcellular localization of AtPABN3, RPL40/UBQ2, and AtDCP5. (a–d) GFP (left), RFP (middle), and merged (right) images of transiently co-transformed onion epidermal cells. DIC images (lower column) reveal the whole cell shapes (a, c, and d). (a and b) Co-localization of AtPABN3-GFP protein with the nuclear speckle marker SRp34-RFP. (c) Co-localization of RPL40/UBQ2-GFP protein with the nucleolar marker AtFbr1-RFP. (d) Co-localization of AtDCP5 protein with the cytoplasmic P-body marker AtXRN4-RFP. Bars are 20 μm (a and c), 10 μm (b), and 50 μm (d). For green fluorescent protein (GFP)-fused constructs, amplified cDNAs were cloned into either the NcoI-SalI or SalI-BsrGI site of the sGFP (S65T) vector (Niwa et al. 1999). For nuclear speckles and P-body markers, SRp34 and XRN4 cDNAs were cloned into pENTR/D-TOPO and then transferred into the destination vector, pH7RWG2.0 (Karimi et al. 2002), using LR clonase II. Primers used for plasmid construction are listed in Supplementary Table 1