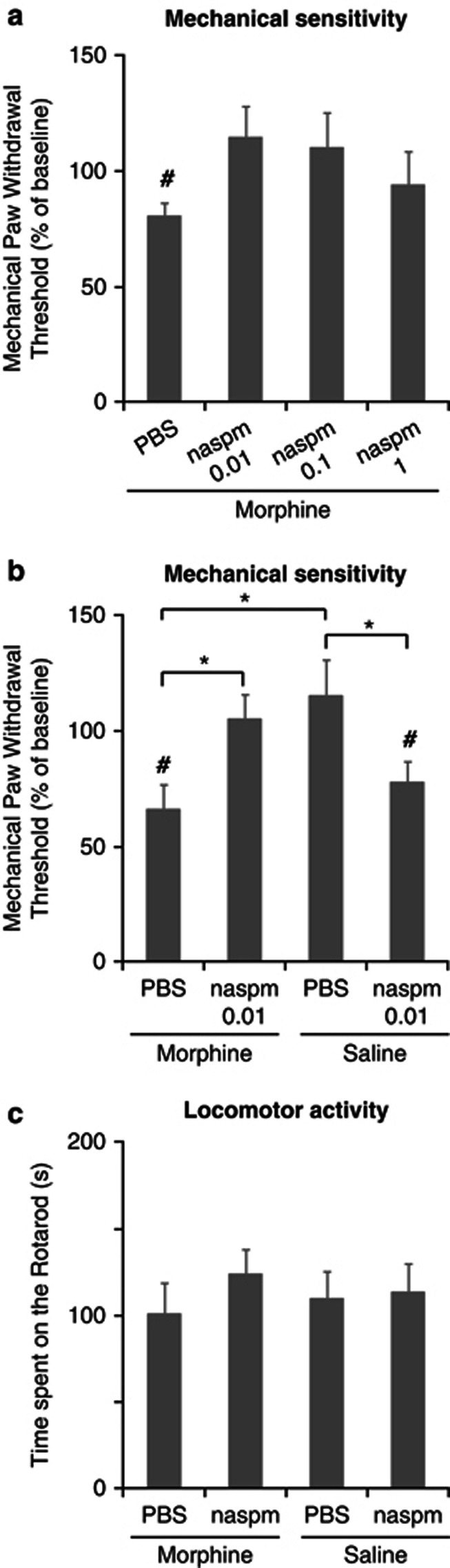
Figure 2.
Intrathecal administration of naspm reverses mechanical hypersensitivity in morphine-treated mice. Twelve hours after repeated morphine or saline administration, mice are injected i.t. with PBS or naspm and evaluated 60 min later. (a) Dose–response relationship for naspm in morphine-treated mice. The PBS group was significantly different from baseline but all naspm groups were not; #p<0.05, vs baseline, paired t-test. (b) 0.01 nmol of naspm reversed mechanical hypersensitivity in morphine-treated mice. The same dose induced a decrease in mechanical thresholds in mice that were not exposed to morphine. Values are expressed as mean %±SEM from the baseline, set to 100; n=7, *p<0.05, two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test; #p<0.05, vs baseline, paired t-test. (c) Motor functions are evaluated by measuring the latency to fall (in s) on the accelerating rotarod. Latencies are similar in all the groups. Values are expressed as mean %±SEM, n=7–9 mice per group, p>0.05, two-way ANOVA.