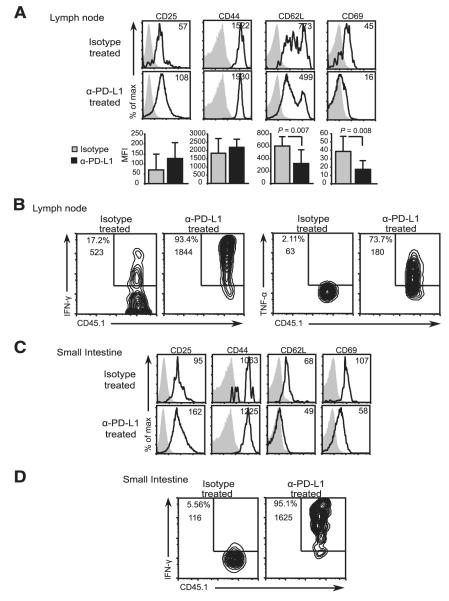
FIGURE 5.
Gut-specific CD8+ T cells acquire effector function upon PD-L1 blockade. Activation of CD45.1+ OT-I T cells in isotype and anti-PD-L1-treated iFABP-tOVA mice. Expression of CD25, CD44, CD62L, and CD69 by donor OT-I T cells (gated on CD8+Vα2+CD45.1+ cells) in lymph nodes (A) and small intestine (C) was analyzed by flow cytometry. Overlays depict the expression of the indicated markers by OT-I T cells (open histogram) from isotype and anti-PD-L1-treated iFABP-tOVA mice compared with isotype Ab staining (gray-filled histogram). Values indicate the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of OT-I T cells for the indicated marker. For each condition, n = 3–6 individual mice were analyzed, and representative histograms are shown. Results represent the mean fluorescence intensity ± SD for the indicated markers on donor OT-I T cells isolated from lymph nodes. Cytokine production by CD45.1+ OT-I T cells in lymph nodes (B) and small intestines (D) from isotype and anti-PD-L1-treated iFABP-tOVA mice analyzed by intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. The n = 3–9 individual mice were analyzed for each condition and representative contour plots are shown. Values at gate indicate percentage of cells among CD8+Vα2+ cells and mean fluorescence intensity for IFN-γ or TNF-α.