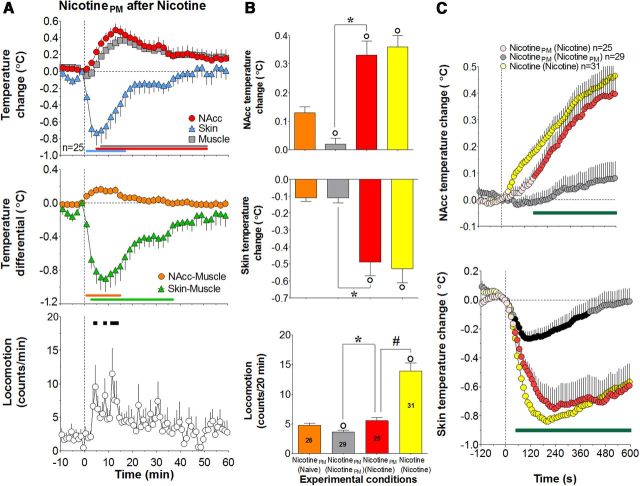
Figure 5.
Nicotine-like effects of nicotinePM after repeated nicotine exposure: temperature and locomotion. A, Top, Mean (±SEM) changes in NAcc, temporal muscle, and facial skin temperatures (°C). Middle, Changes in NAcc–muscle and skin–muscle temperature differentials (°C). Bottom, Locomotor activity (counts/min) induced by intravenous injections of nicotinePM after 2 d of nicotine exposure (°C). n is number of averaged tests. Vertical hatched line represents the start of injection. Horizontal lines of respective colors represent values significantly different from preinjection baseline (p < 0.05; Fisher test). B, Mean (±SEM) changes in NAcc and skin temperatures (°C) and locomotor activity (counts/min) calculated for 20 min after injection. Data are grouped depending upon the drug tested (nicotine and nicotinePM) and previous drug experience: (Naive), no experience (nicotine); (NicotinePM), 2 d of exposure to nicotine or nicotinePM treatment. ○Significant differences compared with nicotinePM in drug-naive conditions (p < 0.05). *Significant differences compared with nicotinePM after nicotinePM injections. #Differences in locomotor effects of nicotinePM and nicotine after nicotine exposure (red and yellow bars, respectively). Numbers of trials in each group are shown within bars. C, Rapid changes in NAcc (top) and skin (bottom) temperatures for 120 s before and 600 s after the onset of intravenous drug injections (vertical hatched line). Filled symbols represent values significantly different from preinjection baseline (p < 0.05). Bold horizontal green lines represent significant between-group differences (p < 0.05).