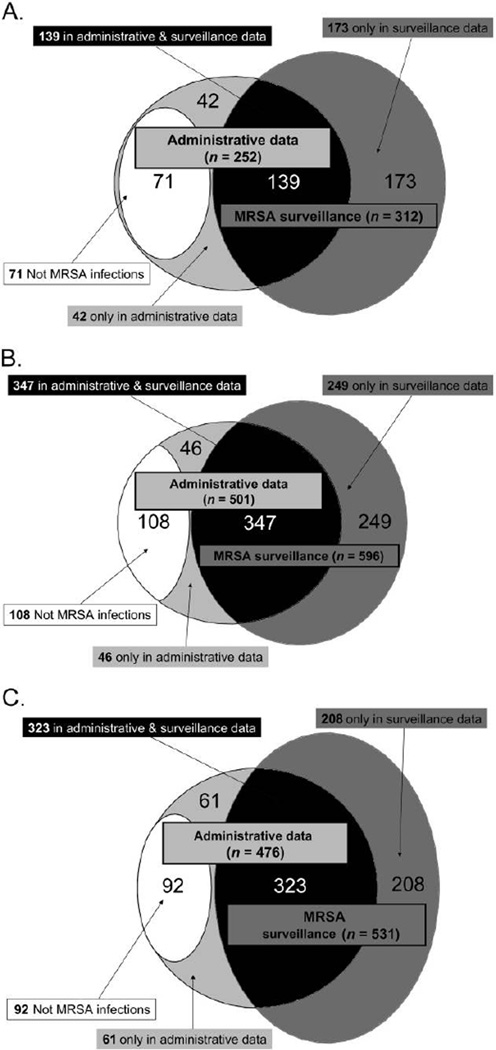
FIGURE 1.
Overlap of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) surveillance data from University of Chicago Medical Center (UCMC) surveillance and University HealthSystem Consortium (UHC) administrative data. A, From July 1, 2004, through June 30, 2005, of the 312 different inpatients identified through clinical microbiology laboratory surveillance who had MRSA infections, 139 were also identified by administrative (billing) data. Of the 252 hospitalized patients identified by administrative data as having an MRSA-related hospital stay, 113 were not identified by surveillance. All of these patients had medical records reviewed: 71 did not have MRSA infections, and 42 did have MRSA infections. The total number of patients with MRSA infections in 2004–2005, then, was 354 (ie, the sum of 173, 139, and 42). A similar analysis was performed for the calendar years 2006 (B) and 2007 (C).