Table 2.
Multiple predictor linear regression for the SWA rebound after sleep deprivation (A,D), the SWA changes from immediately before to after sleep deprivation (B,E), and the SWA changes during spontaneous periods of wake (C,F). A–C, frontal cortex; D–F, parietal cortex. The appropriateness of models to explain the variability in SWA changes was assessed using the Akaike’s information criteria (AIC). For models including multiple predictors, p-values indicate the probability that the corresponding parameter has predictive value when all other parameters are included. AIC and R2 are given for each model; R2 indicates the portion of variance explained by the model and will increase when additional variables are added to a model. AIC is a measure of the relative goodness of fit for a model. More adequately fitting models have lower AIC, but adding poor predictors will increase AIC (indicating a less appropriate model) even if the R2 increases.
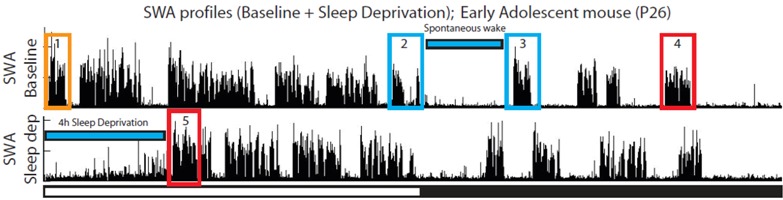 | |||
| (A) Frontal: Predictors for SWA rebound (5/1); % change SWA (5/1) = B0 + (predictors) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.00507 | 362 | 0.189 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.43 | 370 | 0.0164 |
| REM/NREM amount (12 h of recovery) | 0.0071 | 363 | 0.175 |
| n of sleep attempts during sleep deprivation | 0.053 | 367 | 0.0953 |
| Sleep during sleep deprivation (min/4 h) | 0.0582 | 367 | 0.0913 |
| Brief arousals (n/min of sleep, first 4 h of recovery) | 0.31 | 369 | 0.0273 |
| Increase in wake SWA (1–4 Hz) during sleep deprivation | 0.76 | 370 | 0.0249 |
| Slow wave energy (SWE = SWA × time) during deprivation (wake and NREM) | 0.84 | 371 | 0.0011 |
| Time spent awake since last sleep | 0.91 | 371 | 0.00033 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) | 0.000154 | 355 | 0.317 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | <0.0001 | 352 | 0.395 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.0352 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.0009 | 352 | 0.400 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.0297 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.00043 | 352 | 0.431 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) + | 0.17293 | ||
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.14348 | ||
| (B) Frontal: Predictors for SWA change from before to after sleep deprivation (5/4); % change SWA (5/4) = B0 + (parameters) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.00025 | 364 | 0.30 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.64 | 378 | 0.00595 |
| REM/NREM amount (12 h of recovery) | 0.0036 | 369 | 0.20 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.00462 | 369 | 0.19 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.00013 | 362 | 0.324 |
| NREM SWA increase in baseline (4/2) | <0.0001 | 355 | 0.44 |
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.00017 | 350 | 0.53 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.01467 | ||
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.000037 | 346 | 0.575 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.0015 | ||
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.00044 | 344 | 0.615 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) + | 0.00618 | ||
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.06158 | ||
| NR SWA (4/2) × Increase wake alpha (8–12 Hz) + | 0.022 | 340 | 0.669 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.071 | ||
| (C) Frontal: Models Predicting SWA % change (3/2); % change SWA (3/2) = B0 + (parameters) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.913 | 383 | 0.0003 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.39 | 382 | 0.0197 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.016 | 376 | 0.14 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.018 | 377 | 0.139 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) | 0.000047 | 365 | 0.357 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.00039 | 365 | 0.390 |
| Increase in wake alpha | 0.1654 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.000095 | 362 | 0.435 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.029 | ||
| NREM SWA (1/2) × Length of time since last sleep | 0.029 | 358 | 0.506 |
| (D) Parietal: Predictors for SWA rebound (5/1); % change SWA (5/1) = B0 + (predictors) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.0045 | 317 | 0.219 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.46 | 325 | 0.0165 |
| REM/NREM amount (12 h of recovery) | 0.0024 | 315 | 0.246 |
| N of sleep attempts during sleep deprivation | 0.0100 | 318 | 0.185 |
| Sleep during sleep deprivation (min/4 h) | 0.011 | 318 | 0.180 |
| Brief arousals (N/min of sleep, first 4 h of recovery) | 0.62 | 325 | 0.0076 |
| Increase in wake SWA (1–4 Hz) during sleep deprivation | 0.581 | 325 | 0.0093 |
| Slow wave energy (SWE = SWA × time) during deprivation (wake and NREM) | 0.801 | 325 | 0.0020 |
| Time spent awake since last sleep | 0.967 | 325 | 0.0000 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) | 0.0015 | 314 | 0.266 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.00048 | 307 | 0.446 |
| N of sleep attempts during sleep deprivation | 0.00292 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.012 | 312 | 0.360 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.038 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.0033 | 307 | 0.470 |
| N of sleep attempts during sleep deprivation + | 0.0164 | ||
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.2466 | ||
| (E) Parietal: Predictors for SWA change from before to after sleep deprivation (5/4); % change SWA (5/4) = B0 + (parameters) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.0004 | 319 | 0.322 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.51 | 332 | 0.0135 |
| REM/NREM amount (12 h of recovery) | 0.0004 | 319 | 0.320 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.0046 | 324 | 0.219 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.00059 | 320 | 0.304 |
| NREM SWA increase in baseline (4/2) | 0.00056 | 320 | 0.306 |
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.034 | 316 | 0.412 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.023 | ||
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.0039 | 313 | 0.466 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.0041 | ||
| NREM SWA (4/2) + | 0.063 | 311 | 0.526 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) + | 0.010 | ||
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.057 | ||
| NR SWA (4/2) × Increase wake alpha (8-12 Hz) + | 0.100 | 311 | 0.567 |
| Weight-adjusted age | 0.034 | ||
| (F) Parietal: Models Predicting SWA % change (3/2); % change SWA (3/2) = B0 + (parameters) | p | AIC | R2 |
| Weight-adjusted age (using Gompertz fit) | 0.953 | 334 | 0.000 |
| Recovery days from surgery | 0.47 | 334 | 0.016 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.0060 | 326 | 0.207 |
| Increase in wake alpha (8–12 Hz) | 0.133 | 332 | 0.067 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) | 0.0018 | 324 | 0.258 |
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.0061 | 326 | 0.265 |
| Increase in wake alpha | 0.5839 | ||
| NREM SWA decline in baseline (1/2) + | 0.00084 | 316 | 0.444 |
| Length of time since last sleep | 0.00260 | ||
| NREM SWA (1/2) × Length of time since last sleep | 0.026 | 312 | 0.527 |
