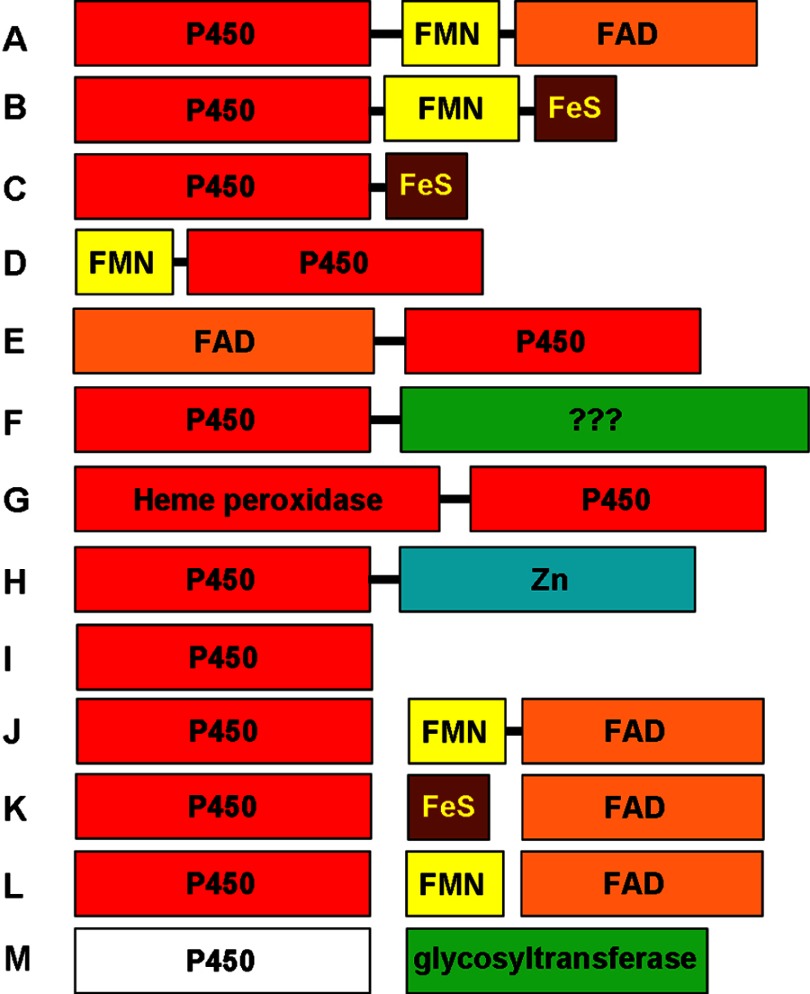
FIGURE 4.
Diversity of P450 redox systems and P450 fusion proteins. A selection of distinct types of P450 enzymes and (where relevant) their redox partner systems is shown. The sizes of the boxes are indicative of the lengths of the protein modules. Bound prosthetic groups are indicated in the color-coded domains. A, P450BM-3 (CYP102A1)-type P450-CPR fusion, also seen for fungal P450foxy (CYP505)-type systems (54). B, CYP116B-type P450-phthalate dioxygenase reductase fusion (55). C, M. capsulatus P450-FDx fusion CYP51FX (56). D, R. rhodochrous P450-flavodoxin fusion XplA, involved in reductive degradation of explosives (57). E, Pseudomonas fluorescens PfO-1 acyl-CoA dehydrogenase-P450 fusion CYP222A1. This protein is depicted with FAD bound in its N-terminal domain, but there is no report to date of characterization of this protein. F, Mimivirus CYP5253A1, with a P450 fused to a C-terminal domain of uncertain function but containing several potential sites for post-translational modification. G, PpoA dioxygenase/peroxidase-P450 fusion enzyme from A. nidulans, involved in Psi factor production (58). H, P450-hydrolase fusion CYP631B5, involved in mycophenolic acid production (59). I, “stand-alone” P450 that acts without partner proteins, typified by P450nor (CYP55A)-type nitric-oxide reductase enzymes that interact directly with NAD(P)H, peroxygenase CYP152 P450s that use H2O2 to oxidize substrates, P450s that isomerize substrates (e.g. CYP5A1/8A1), and allene oxide synthase (CYP74A) dehydratase P450s. J, typical eukaryotic Class II P450 systems with separate membrane-associated P450 and a CPR partner. K, Class I (mitochondrial) P450 system that interacts with the iron-sulfur protein ADx, which is in turn reduced by ADR. Most bacterial systems use a similar redox apparatus (60). L, variation on system K, in which a flavodoxin replaces the iron-sulfur protein. This type of system supports CYP176A1 (P450cin); enables Citrobacter braakii to catabolize cineole; and can also reduce CYP107H1 (P450BioI), involved in B. subtilis biotin synthesis (61, 62). M, heme-free EryCII P450-like protein devoid of a cysteine proximal ligand. EryCII is an allosteric activator of the glycosyltransferase EryCIII in the production of erythromycin D in S. erythraea (63).