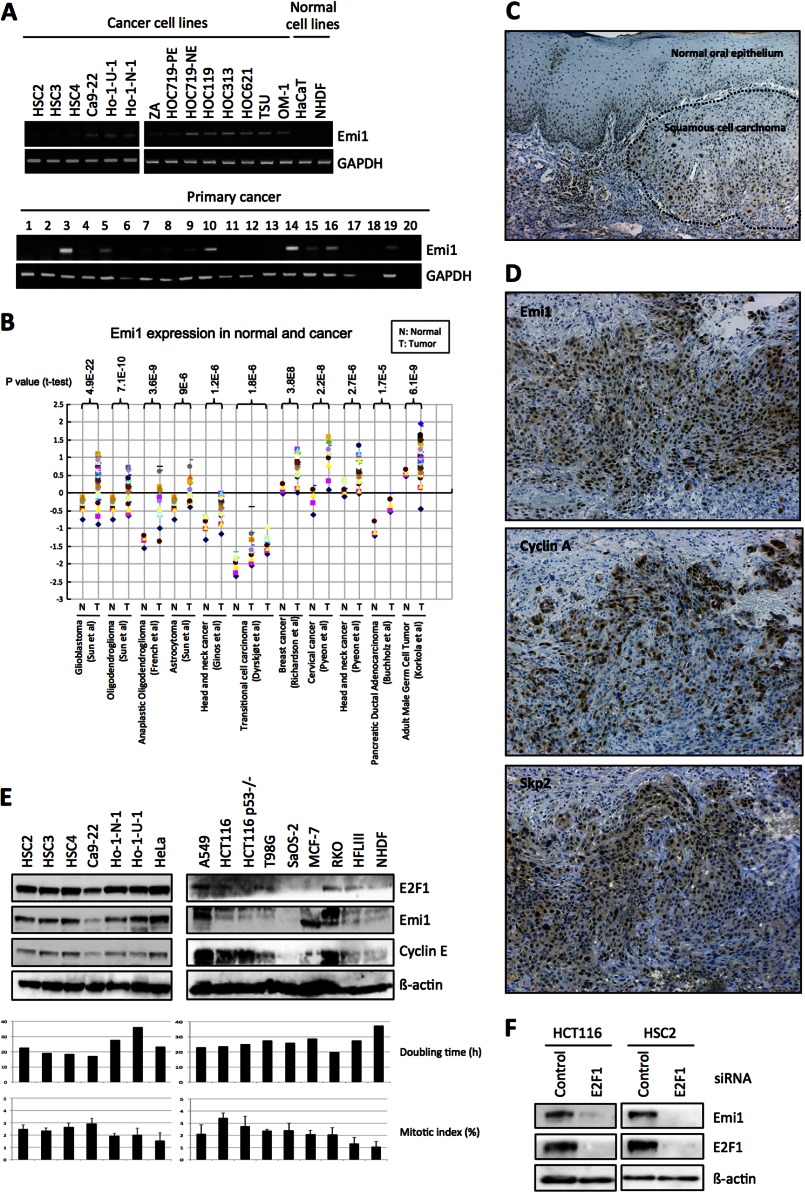
FIGURE 1.
Emi1 overexpression in head and neck cancer. A, Emi1 mRNA expression was examined in 14 head and neck cancer cell lines, 2 normal cells, and 20 head and neck cancer tissues by RT-PCR. GAPDH was used as a control. B, mRNA level of Emi1 in different human tumors. All data were provided by the Oncomine database. Data from Refs. 43–50 were reanalyzed to show expression level of Emi1 in normal brain, glioblastoma, oligodendroglioma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, head and neck cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, cervical cancer, transitional cell carcinoma, and adult male germ cell tumor (43–50). N, normal tissues; T, tumor tissues. C, immunohistochemical expression of Emi1 in head and neck cancer. D, correlation between Emi1 expression and APC substrates, cyclin A, and Skp2 expression. We examined the expression of Emi1, cyclin A, and Skp2 in head and neck cancer cases. A representative head and neck cancer case is shown. E, high expression of Emi1 is regulated by E2F1 in cancer cells. Expression of Emi1, E2F1, and cyclin E was examined by Western blot analysis in cancer cell lines (HSC2, HSC3, HSC4, Ca9–22, Ho-1-N-1, Ho-1-U-1, HeLa, A549, HCT116, HCT116 p53−/−, T98G, SaOS-2, MCF-7, and RKO) and normal cells (HFL III and NHDF). β-Actin expression was used as a loading control. The graph shows the mitotic index (%) and doubling time (h) in each cell. F, E2F1 siRNA was transfected into HCT116 and HSC2 cells. After 48 h of E2F1 siRNA treatment, cells were collected. Emi1 and E2F1 expression was examined by Western blot analysis. β-Actin expression was used as a loading control.