FIGURE 6.
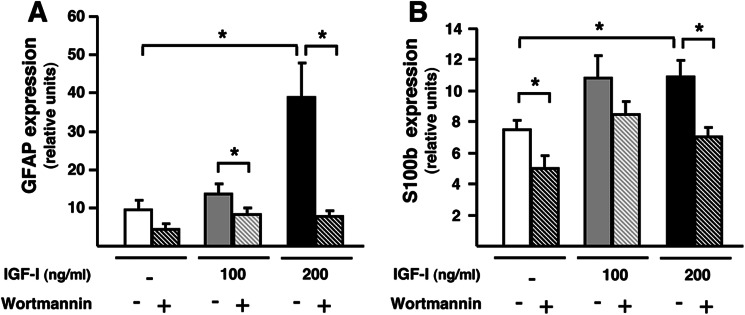
Increased gliosis in wild-type retinas exposed to recombinant IGF-I. A, GFAP; B, S100b expression levels in WT retinas incubated with increasing concentrations of IGF-I in the presence or absence of wortmannin, an inhibitor of IGF-I downstream signaling. The expression of both markers of gliosis was increased in the presence of IGF-I, and this effect was abrogated by the addition of wortmannin. Values are expressed as the mean ± S.E. of 3–4 retinas/group. *, p <0.05.
