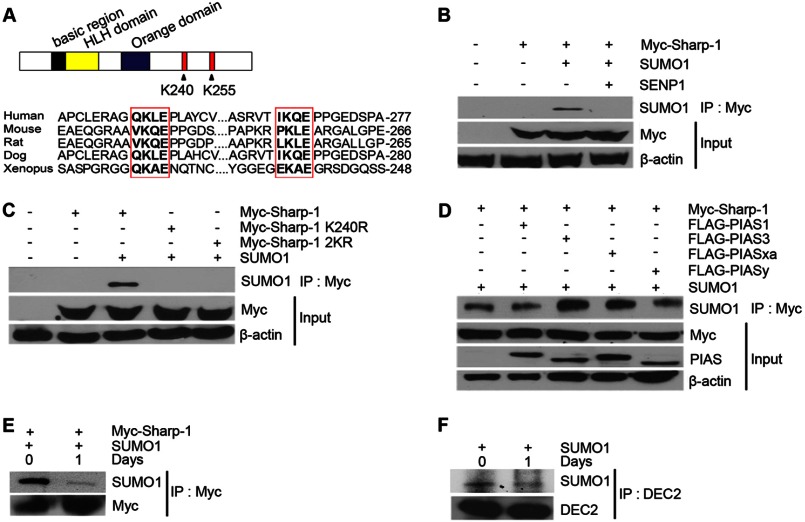
FIGURE 1.
Sharp-1 is SUMO-modified. A, the domain structure Sharp-1 is shown with the basic, helix-loop-helix (HLH), and the Orange domains (upper panel). Potential sumoylation sites at Lys-240 and Lys-255 are indicated. Alignment of the two SUMO consensus motifs in Sharp-1 cDNA from human, mouse, rat, dog, and Xenopus showed high conservation across species. B, cells were co-transfected with constructs encoding Myc-Sharp-1, SUMO-1, and SENP1 as indicated. Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with Myc-agarose beads followed by immunoblotting with anti-SUMO-1 antibody. Anti-Myc antibody was used to detect expression of Sharp-1. β-Actin served as a loading control. C, cells were co-transfected with Myc-Sharp-1, Sharp-1 K240R, and Sharp-1 2KR along with SUMO-1. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with Myc-agarose beads followed by Western blotting with anti-SUMO-1 antibody. D, FLAG-tagged PIAS1, PIAS3, PIASxα, and PIASy were co-transfected with Myc-Sharp-1 and SUMO-1. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Myc-agarose beads, and immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blotting with anti-SUMO-1 antibody. Sharp-1 and PIAS proteins were detected with anti-Myc and anti-FLAG antibodies, respectively. E, C2C12 cells were co-transfected with Myc-Sharp-1 and SUMO-1. Cells were harvested as undifferentiated cells (day 0) and 1 day after differentiation (day 1), immunoprecipitated with Myc-agarose beads followed by Western blotting with anti-SUMO-1 and anti-Myc antibodies. F, C2C12 cells were transfected with SUMO-1. Endogenous Sharp-1 was immunoprecipitated from day 0 and day 1 lysates using anti-DEC2 (Sharp-1) antibody followed by Western blotting with anti-SUMO-1 antibody.