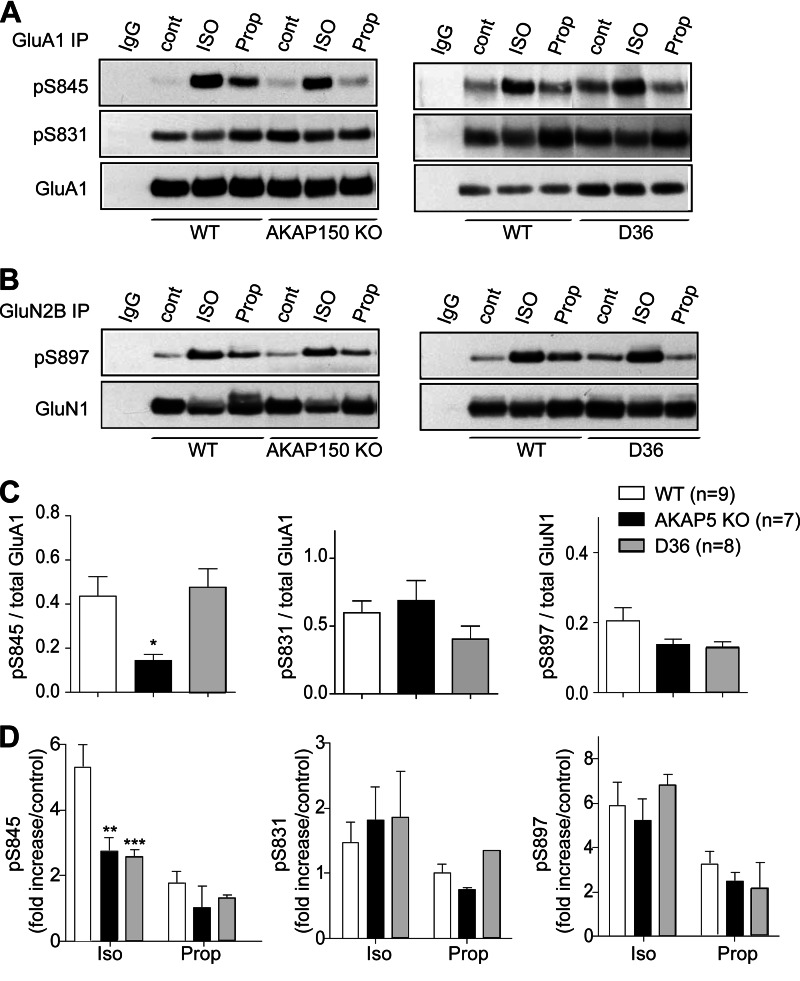
FIGURE 3.
AKAP5-anchored AC is required for phosphorylation of GluA1 on Ser-845 upon β2-AR stimulation. A and B, acute forebrain slices from 8–12-week-old WT C57BL/6, AKAP5 D36, and AKAP5 KO mice were incubated with vehicle, ISO (10 μm), or ISO plus propranolol (Prop) (1 μm) for 5 min before extraction, IP of GluA1, and immunoblotting with antibodies against phospho-Ser-845 (pS845), phospho-Ser-831 (pS831), and total GluA1 (GluA1) (A) or IP of the NMDA receptor with an antibody against the GluN2B subunit and immunoblotting with antibodies against phospho-S897 (pS897) and total GluN1 (GluN1) (B). IgG, control IPs with nonspecific rabbit IgG to ensure specificity of GluA1 and GluN2B IPs. C and D, immunosignals were quantified for phospho-Ser-845, phospho-Ser-831, and phospho-Ser-897 and corrected for variations in total GluA1 and GluN1 loading. Graphed are averages ± S.E. (error bars) of relative phosphorylation levels under basal conditions (C) and averages ± S.E. of -fold increases by ISO and ISO + propranolol (Prop) versus basal phosphorylation levels (D) for each genotype (bottom bar diagrams). The number n (C, top right) indicates the number of independent experiments (for each experiment, one mouse per genotype was used; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 for KO or D36 versus WT). ISO significantly increased GluA1 Ser-845 and GluN1 Ser-897 phosphorylation, and propranolol antagonized these increases in all three genotypes (the statistically significant treatment effects are not depicted in the graphs for simplicity). Neither treatment affected Ser-831 phosphorylation in any genotype. Basal GluA1 Ser-845 phosphorylation was decreased for KO but not D36 versus WT (one-way ANOVA (p = 0.0375); Tukey's multiple comparison test for WT versus KO (p < 0.05) and for WT versus D36 (p > 0.05)). ISO-induced -fold increase of Ser-845 phosphorylation was decreased for KO and for D36 versus WT (two-way ANOVA for genotype (p = 0.0243) and for treatments with ISO and ISO + propranolol (p = 0.0012); Bonferroni post-test for ISO treatment for WT versus KO (p < 0.01) and for WT versus D36 (p < 0.001); p > 0.05 for both comparisons for ISO + propranolol treatment). Basal GluA1 Ser-831 phosphorylation was unaltered in KO and D36 versus WT mice (one-way ANOVA p = 0.2639). ISO did not increase Ser-831 phosphorylation in any of the three genotypes (two-way ANOVA, p = 0.8826 for genotypes and p = 0.2658 for treatments). The slight decrease in basal GluN1 Ser-897 phosphorylation in KO and D36 versus WT was statistically not significant (one-way ANOVA, p = 0.2242). ISO-induced increases in Ser-897 phosphorylation were comparable for all three genotypes (two-way ANOVA, p = 0.7098 for genotypes and p = 0.0001 for treatments).