Figure 3. Signal transduction events resulting in pathologic trypsinogen activation and NFkB activation.
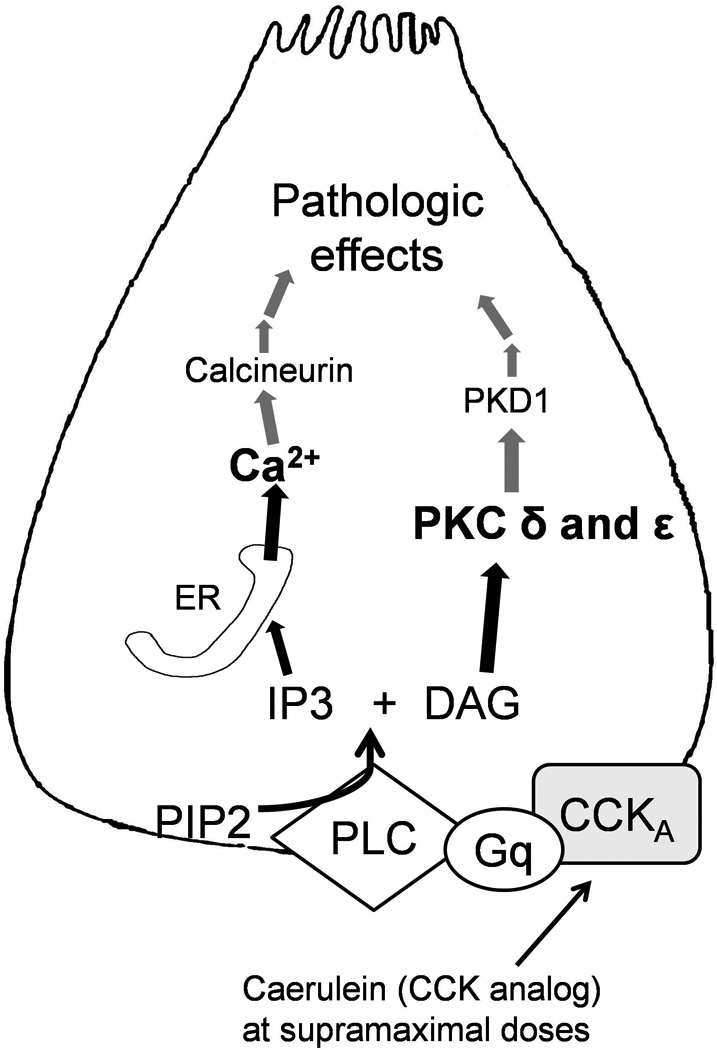
Cholecystokinin analog Caerulein induced pancreatitis has been used as a model in this schematic. CCKA: Cholecystokinin receptor subtype A, Gq: G-protein q subtype; PLC: phospholipase C, PIP2: Phosphoinositol 4-phosphate, IP3: Inositol-3 Phosphate, DAG: Diacylglycerol; PKC: protein kinase C, PKD: protein kinase D. Caerulein (CCK analog) binds to its receptor as shown and leads to generation of IP3 and DAG. IP3 opens ER membrane IP3 receptors which are implicated in physiologic calcium signaling. Calcium released through IP3R leads to opening of RyRs as described in figure 2. The grey lines in the figure depict either unknown steps or proposed mechanisms awaiting verification in future studies.
