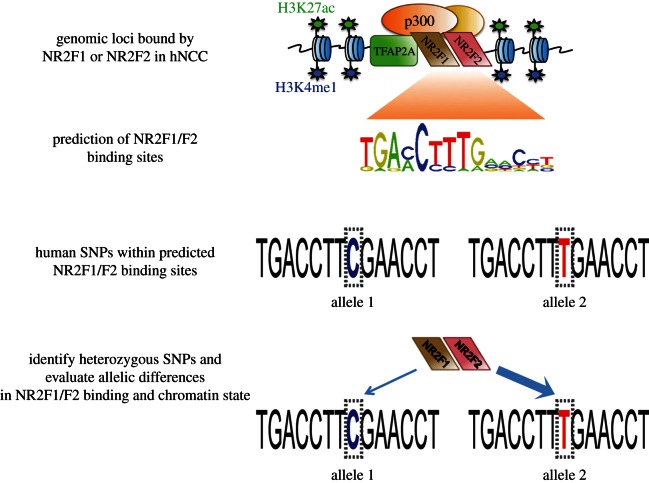
Figure 2.
Strategy for using human genetic variation as a tool to investigate binding cooperativity between NR2F1/F2 and TFAP2A at hNCC enhancers. Location of NR2F1/F2 binding motif within distal genomic sites bound by NR2F1 or NR2F2 in hNCC (n = 2748, reported in [44]) was predicted using the ‘MISP:Motif-based interval screener with PSSM’ tool from Cistrome (http://cistrome.org/ap/), which resulted in 4712 predicted NR2F1/F2 sites. For site predictions, the NR2F1/F2 motif IDs used were MA0017, M00155, UP00009 with a cut-off of 100 for the motifs screen. Next, all human SNPs (based on dbSNP build 130) overlapping the predicted NR2F1/F2 binding sites were identified (n = 373). Then, 19 SNPs of high heterozygosity within human population were selected and genotyped in H9 hESC, yielding nine heterozygous SNPs. hNCC were derived from H9 hESC, and ChIP and quantitative genotyping were combined in order to evaluate allelic differences in TF binding and active enhancer chromatin marks at these heterozygous loci.