Fig. 3. RavZ functions as a cysteine protease that specifically deconjugates Atg8 proteins from phospholipid membranes.
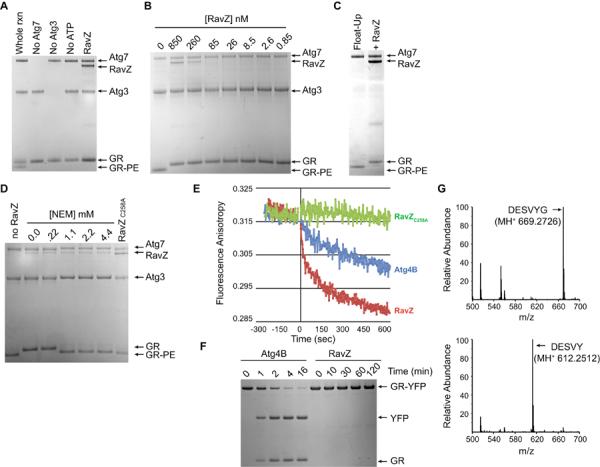
(A) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel from an in vitro GR conjugation assay containing the conjugating enzymes Atg7 and Atg3, the RavZ protein, the unconjugated GR protein and the lipid-conjugated GR protein (GR-PE). Lanes from the whole reaction (rxn) and reactions missing individual components are marked. The RavZ lane contained all the components of the whole rxn plus purified RavZ protein. (B) Indicated above each lane are the concentrations of purified RavZ added to a conjugation assay containing GR at a concentration of 12 μM. (C) Liposomes containing GR conjugated to PE were isolated on a flotation gradient (Float-Up lane) and treated with RavZ (+RavZ lane). (D) Liposomes containing GR-PE were treated with RavZ in the presence of the indicated concentrations of NEM or were treated with the RavZC258A protein. (E) Fluorescence anisotropy was used to analyze the release kinetics of Texas-Red-labeled GR from liposomes in vitro upon treatment with RavZ (red line), Atg4B (blue line), and RavZC258A (green line). (F) Stained SDS-PAGE gels show that GR-YFP was rapidly cleaved by Atg4B to generate the products GR and YFP. No cleavage of GR-YFP was observed by RavZ after a 120 min reaction. (G) LC-MS/MS chromatographs from samples containing purified GR (top graph) and GR that was isolated after RavZ-mediated deconjugation from PE-containing liposomes (bottom graph). Arrow indicates that the native C-terminal peptide in GR (DESVYG) was abundant in the untreated sample and that RavZ-mediated deconjugation resulted in a loss of the C-terminal glycine (DESVY).
