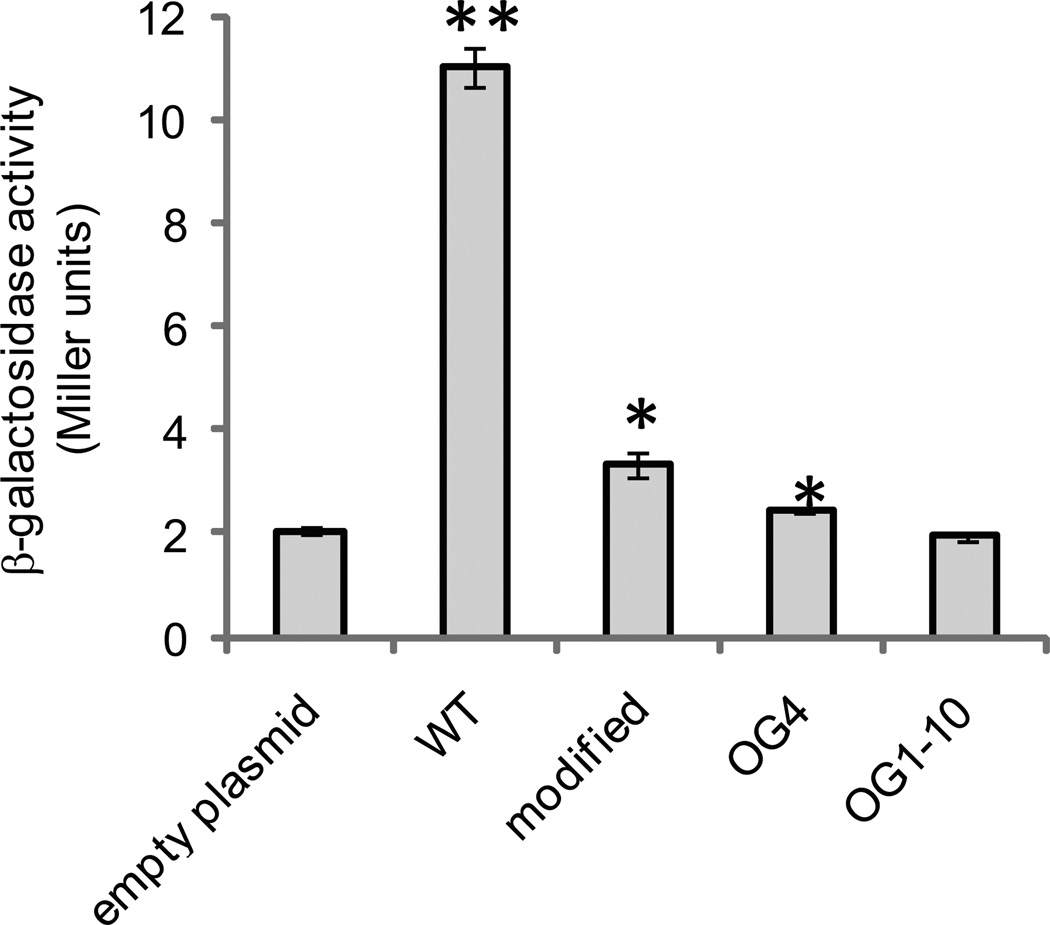
Figure 2.
In vivo assay for NsrR binding to the aox promoter region. β-galactosidase assays were performed on AKD712 (chromosomal aox-lacZ fusion strain) containing either an empty control plasmid (pAKD700), pAKD700 containing approximately 200 bp of the DNA sequence upstream of the start codon encoded by aox (WT; pAKD750), pAKD700 containing a PCR-modified aox promoter region (modified; pAKD751), and pAKD700 containing the aox promoter region PCR-amplified from either suppressor mutant OG4 or OG1-10. Sequences are shown in Fig. 1. Plasmids are maintained at ∼10 copies per chromosome, and when they contain an NsrR binding site will effectively titrate out NsrR, relieving repression of aox transcription and resulting in production of LacZ. Cells were grown to mid-log phase in mineral-salts medium containing GlcNAc prior to harvesting for the assay. Data are the average of three independent cultures from one representative experiment. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. The experiment was repeated three times. Asterisks indicate significant differences in mean activity compared to the pAKD700 control as determined using a student’s t-test. ** p < 0.01; * p<0.05