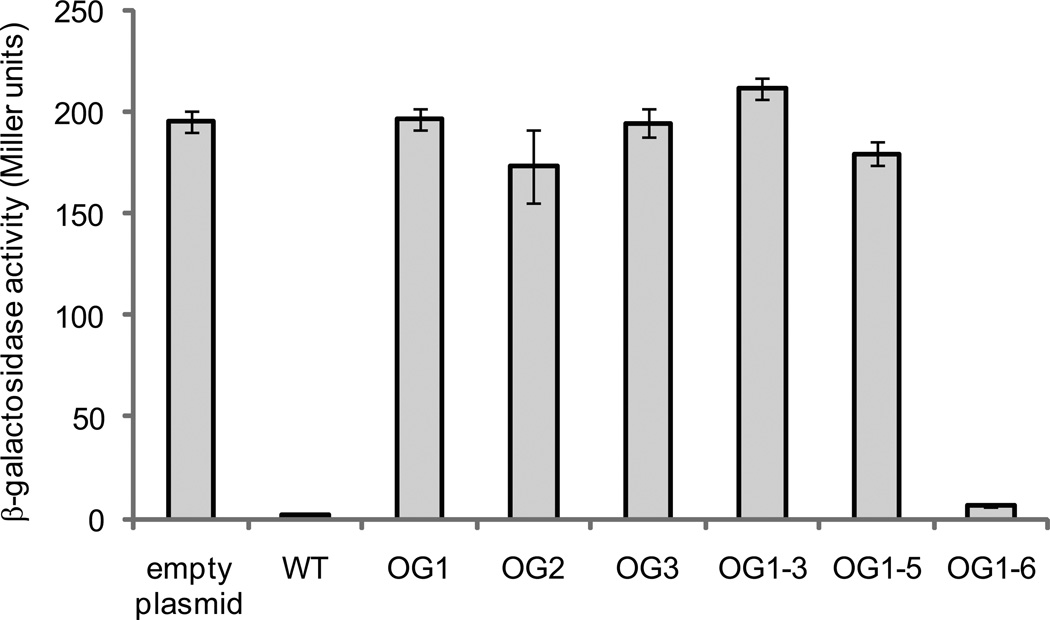
Figure 3.
In vivo assay for NsrR activity. β-galactosidase assays were performed on AKD785 (nsrR mutant, chromosomal aox-lacZ fusion strain) in which NsrR variants were overexpressed. nsrR genes from wild type and ΔcydAB suppressor mutants were cloned into pAKD601B, placing expression under the control of an IPTG-inducible promoter. Cells were grown in LBS medium overnight in the presence of kanamycin and IPTG before harvesting for the assay. High levels of β-galactosidase activity indicate a non-functional version of NsrR that can no longer bind to the aox promoter region and repress expression of lacZ. Bars are labeled with the name of the suppressor mutant from which the variant nsrR was isolated, along with the wild-type (WT) and empty plasmid controls. Data are the average of three independent cultures from one representative experiment. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate significant differences in mean activity compared to the wild-type control as determined using a student’s t-test (p < 0.01). The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.