Figure 1.
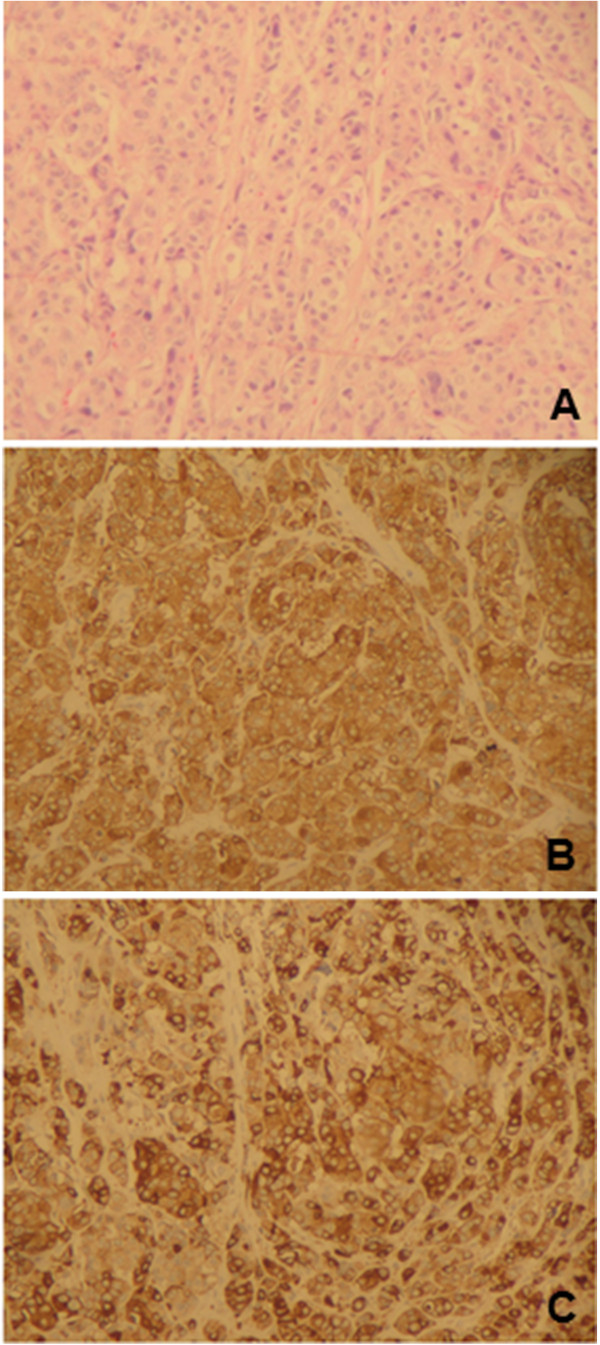
Histopathological findings of the primary alveolar-type neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast. The tumor showed solid nests of cancer cells growing in alveolar-like patterns, which were separated by fibrovascular stroma and collagen and infiltrated the ducts and ductules (A). The neuroendocrine tumor component showed diffuse positive immunoreactivity to chromogranin A (B) and synaptophysin (C) (original magnification: A: 10× and B, C: 40×).
