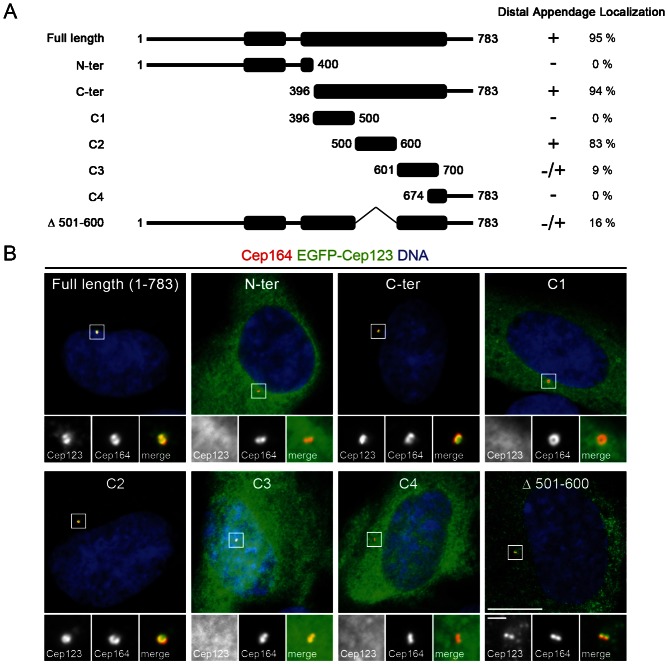
Fig. 2. Mapping of the distal appendage-targeting domain in Cep123.
(A) A diagram showing the EGFP-Cep123 fragments used to identify the distal appendage-targeting domain in Cep123. (B) Immunofluorescent images of RPE1 cells transfected with the EGFP-Cep123 constructs (green) and stained with DAPI (blue) and an antibody against the distal appendage component Cep164 (red). The C2 fragment (residues 500–600) was able to localize to the distal appendages with a similar efficiency as the full length protein. This domain was not essential for the targeting of Cep123 to the distal appendages, although it increased the fidelity of proper localization. Scale bars: 10 µm and inset 1 µm.