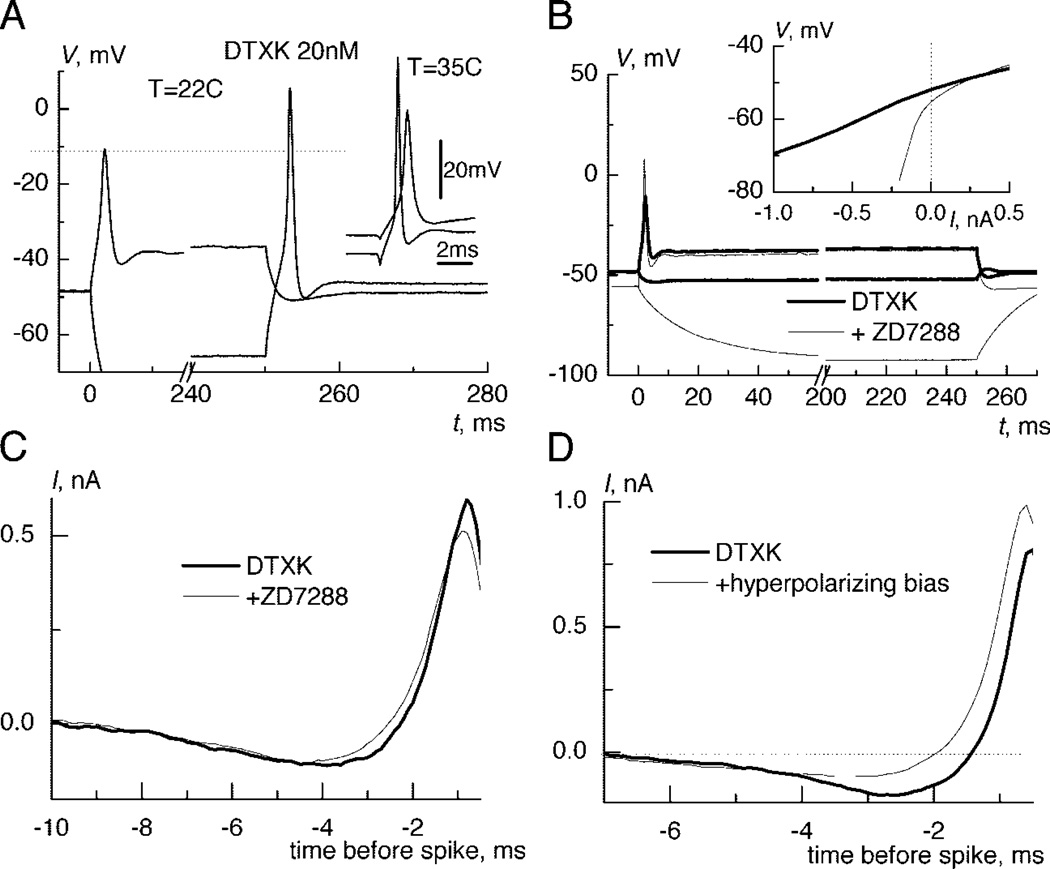
FIG. 3.
Influence of Ih on response properties and the integration of small signals. A: the amplitude of rebound spikes after hyperpolarizing injection of −1 nA are larger than that of spikes evoked by depolarizing injection of 0.8 nA even after application of DTXK. Inset: the same was true for spikes evoked by threshold current injections (0.4 and 1 nA) from rest or during hyperpolarization by −0.75 nA at 35°C. B: an Ih antagonist (ZD7288) hyperpolarized neurons but did not change the response to a depolarizing current step. Inset: steady current-voltage relation shows that ZD7288 blocked a large portion of the hyperpolarization activated current. C: spike-triggered reverse-correlation current changed very little after ZD7288 because the integration was defined by remaining IKLT an INaD: injection of hyperpolarizing bias current reduced the dip. Offsets were subtracted in D and C.