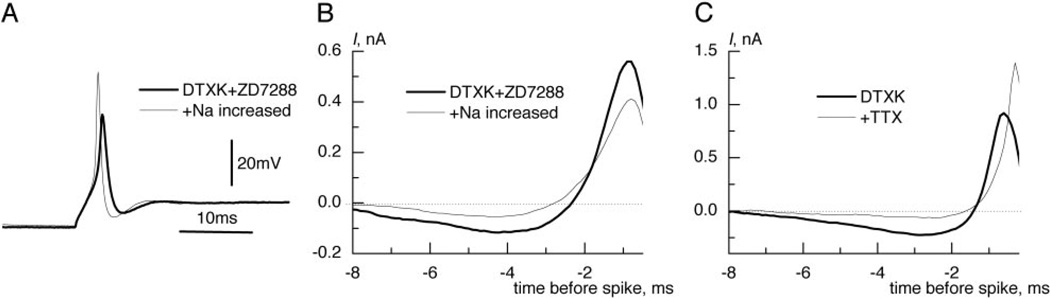
FIG. 4.
Sodium current strongly influenced integration of small signals. A: increase of extracellular sodium concentration by 30%, in addition to DTXK and ZD7288, made inward current stronger and enlarged the spike. B: strengthening of sodium current reduced the dip and slowed the rise of the reverse-correlation current. C: after addition of TTX, reverse correlation was triggered by crossings of depolarized potential level. Note that the dip almost disappeared, suggesting that it was needed to reduce inactivation. Offsets were subtracted in B and C.