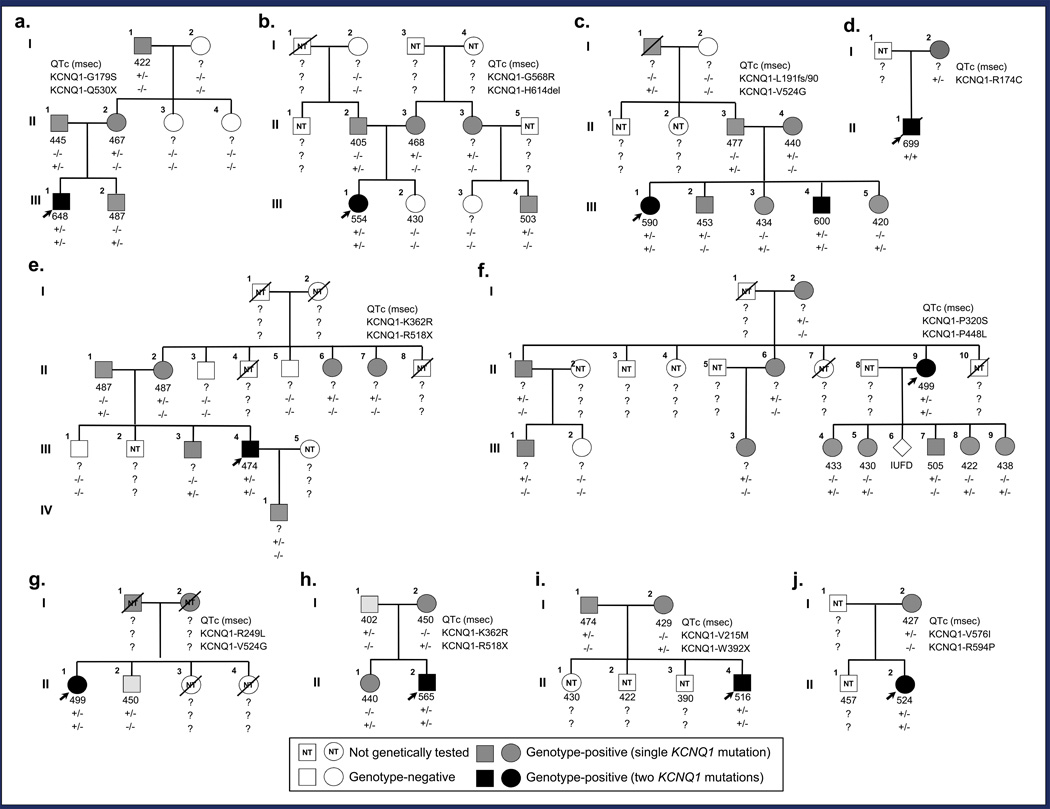
Figure 1.
Pedigree structure and genotypic information for families of KCNQ1 homozygotes/compound heterozygotes with intact hearing. Genotype-positive individuals indicated by gray (single KCNQ1 mutation) or black (two KCNQ1 mutations) squares (male) and circles (female). Genotype-negative individuals indicated by open symbols; index cases by black arrows; and deceased individuals by slashes. Lastly, squares or circles containing “NT” (not tested) indicate individuals who have yet to undergo or have refused genetic testing. QTc intervals and genotypes are displayed beneath each symbol. a. Family AR LQT1a. This three-generation pedigree is notable for the index case with severe QT prolongation that suffered from breakthrough syncopal episodes prior to undergoing a LCSD (III.1). b. Family AR LQT1b. This three-generation pedigree is notable for the index case with severe QT prolongation and a history of breakthrough cardiac events (III.1). c. Family AR LQT1c. This three-generation pedigree is notable for the index case with severe QT prolongation and a history of breakthrough cardiac events including an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (III.1) and her brother who also has severe QT prolongation and has suffered multiple breakthrough cardiac events including an ICD storm (III.4). d. Family AR LQT1d. This two-generation pedigree is notable only for the index case that displays extreme QT prolongation and suffered multiple breakthrough cardiac events prior to succumbing to his malignant LQTS phenotype at the age of 3 (II.1). e. Family AR LQT1e. This four-generation pedigree is notable for the index case with QT prolongation that suffered numerous exertional syncopal episodes during childhood (III.4). f. Family AR LQT1f. This three-generation pedigree is notable for the index case who features a prolonged QT interval but has remained asymptomatic for the last 25 years (III.9) and the sudden unexplained deaths of her siblings at the age of 13 and 3, respectively (III.7 and III.10). g. Family AR LQT1g. A two-generation pedigree notable for the index case with QT prolongation (III.1) and the swimming-triggered sudden unexplained death of the index case’s 13-year old sister (III.3). h. Family AR LQT1h. A two-generation pedigree notable for the index case who has severe QT prolongation and suffered several breakthrough ICD shocks prior to undergoing a LCSD (III.2). i. Family AR LQT1i. This two-generation pedigree is notable for the index case who has QT prolongation and suffered several breakthrough cardiac events including an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (III.5). j. Family AR LQT1j. This two-generation pedigree is notable for the symptomatic index case that has QT prolongation (III.2).