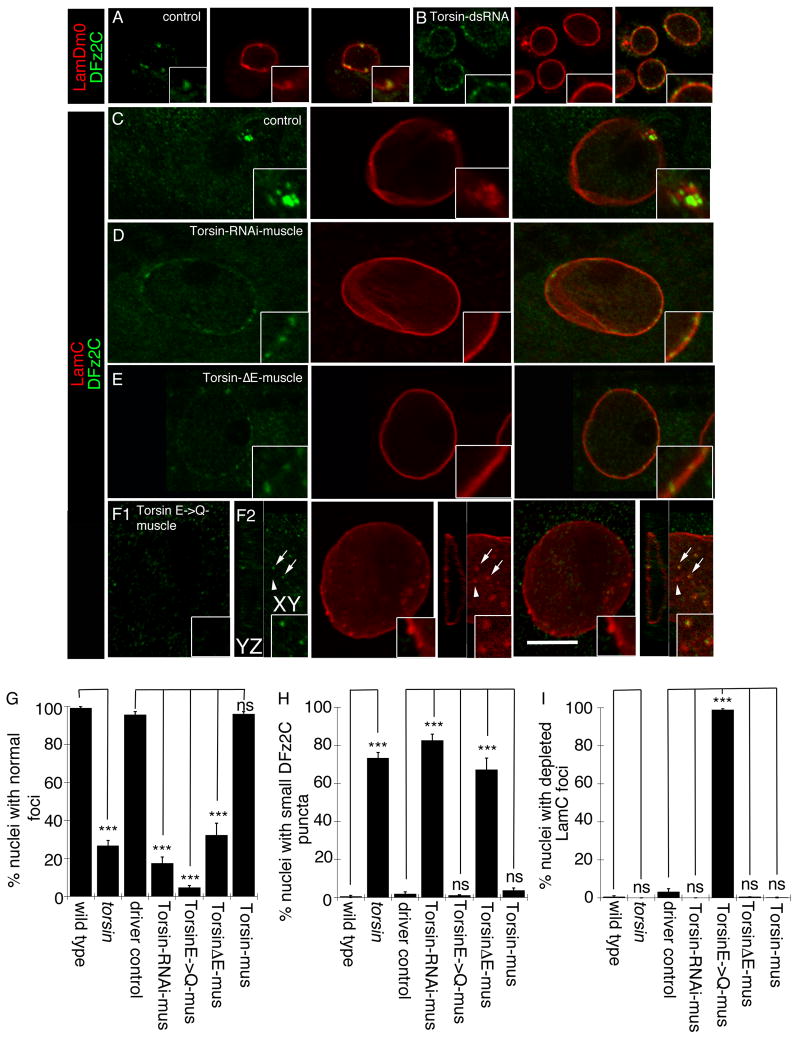
Figure 1. Morphology of nuclear DFz2C/Lam foci is disrupted in Torsin mutations.
(Also see Fig. SF1). (A, B) Localization and morphology of DFz2C/Lam foci at the nuclei of S2 cells in (A) untreated cells, and (B) cells treated with Torsin-dsRNA. (C–F) Localization and morphology of nuclear DFz2C/LamC foci in larval muscles of (C) wild type and (D–F) larvae expressing (D) Torsin RNAi, (E) TorsinΔE, and (F) TorsinE→Q in muscles. F1 is a low magnification view. F2 shows a high magnification view of DFz2 puncta in the YZ and XY planes. (A–F) correspond to singe confocal slices. (G–I) Percentage of nuclear foci showing (G) normal organization of DFz2C/LamC, (H) the presence of small DFz2C puncta associated with the lamina (see text), and (I) the presence of thickenings of the lamina devoid of DFz2C signal. mus= muscle. N([number of nuclei;number of larvae])= [908;6],[731;6],[639;6],[802;6],[846;6],[733;6],[693;6]. Error bars represent ± SEM (***: p<0.0001). Calibration scale (μm)=A,B:14, (4μm for insets); C–F:10 (6μm for insets).