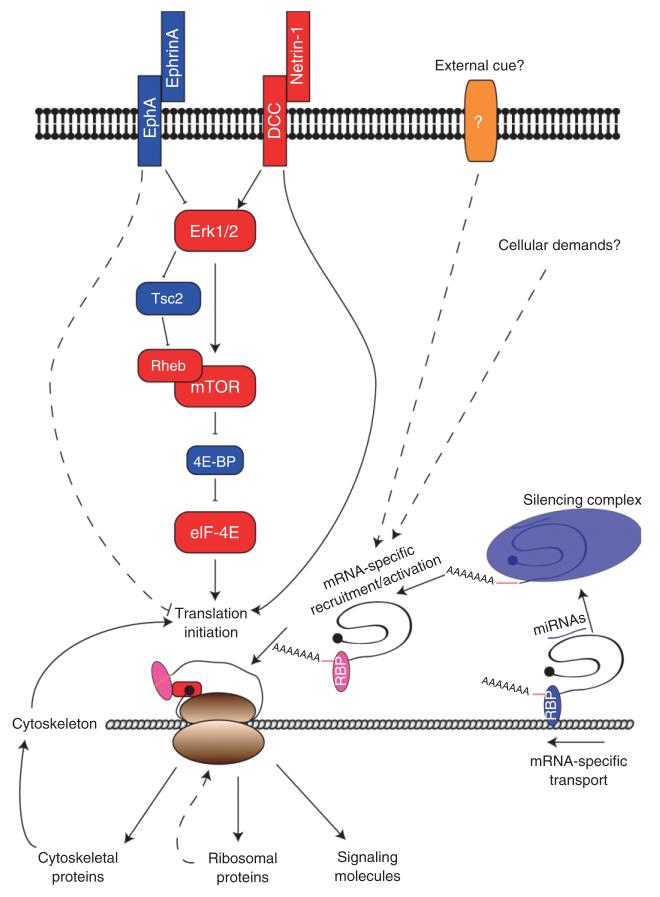
FIGURE 1.
Regulation of local mRNA translation in growth cones. Growth cones integrate multiple external signals that increase or decrease mRNA translation activity. In general, mRNA translation is regulated at the level of eIF-4E, which activates cap-dependent translation initiation. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) induces phosphorylation of 4E-BP, an inhibitor of eIF-4E, and subsequently relieves repression of translation initiation. mTOR is regulated by the small GTPase Rheb, and can be inhibited by signals that activate Tsc2, the Rheb GTPase activating protein (GAP). Tsc2 is negatively regulated by Erk1/2 MAP kinase and therefore activation of Erk1/2 results in activation of mTOR. Erk1/2 can also directly phosphorylate 4E-BP. For example, Netrin-1 increases mRNA translation by activating Erk1/2, whereas EphrinA decreases mRNA translation by inhibiting Erk1/2. Alternatively, binding of Netrin-1 to DCC may directly activate translation by regulating the direct association between DCC and translation machinery. It remains to be seen whether any external signals negatively regulate translation also by directly associating with translational machinery (e.g., EphA). Translation machinery is in physical contact with cytoskeletal networks where translation occurs. Local translation of cytoskeletal proteins regulates cytoskeletal dynamics, and the changes in cytoskeleton can also regulate the degree of local translation. Local translation of ribosomal proteins may occur to replenish or repair ribosomes. A subset of mRNAs are transported along cytoskeleton to growth cones by associating with RNA binding proteins (RBPs), which then bind to motor proteins. Specific cis-elements in the 5′- or 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs) are recognized by RBPs. Most mRNAs in growth cones are translationally repressed and signals may regulate release of certain mRNAs from repression. MicroRNAs may participate sequence-specific repression and derepression of mRNA translation.