Fig. 5.
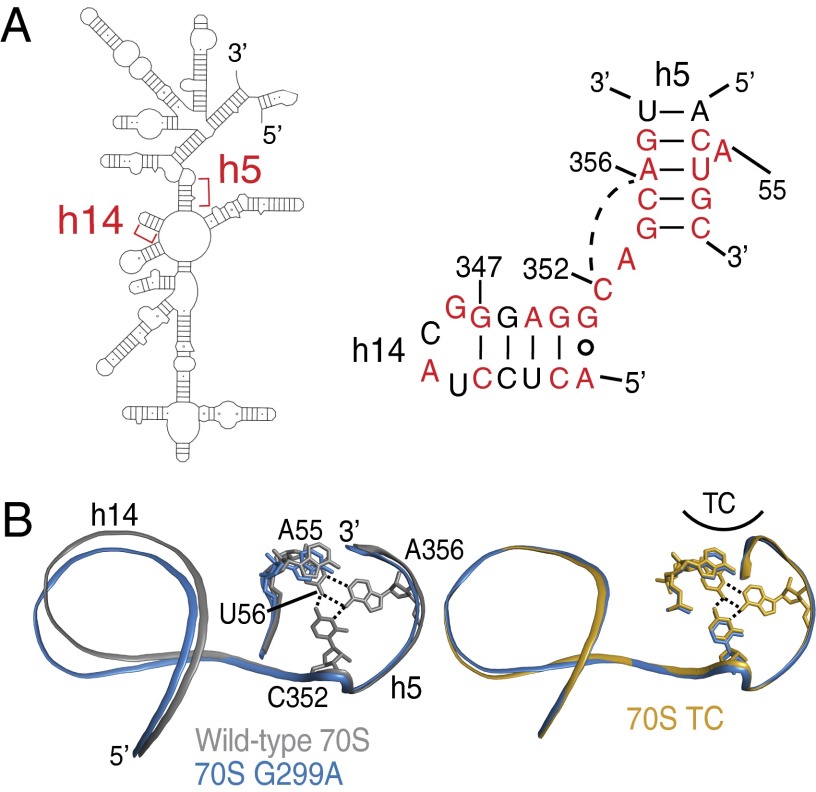
Conformational changes in h14 are propagated to h5. (A) An overview of the 5′ domain of 16S rRNA (Left) with the secondary structure diagram of the junction between h5 and h14 of 16S rRNA (E. coli numbering; Right). Nucleotides conserved at >90% in all cytoplasmic ribosomes are colored red (36). The base triple between C352 and the U56⋅A356 base pair is illustrated with a broken line. (B) A comparison of 70S G299A and either wild-type 70S (Left) or 70S TC (Right) reveals how the mutant ribosomes are poised for productive interaction of h5 with EF-Tu, whereas wild-type 70S are less organized for interactions with EF-Tu.