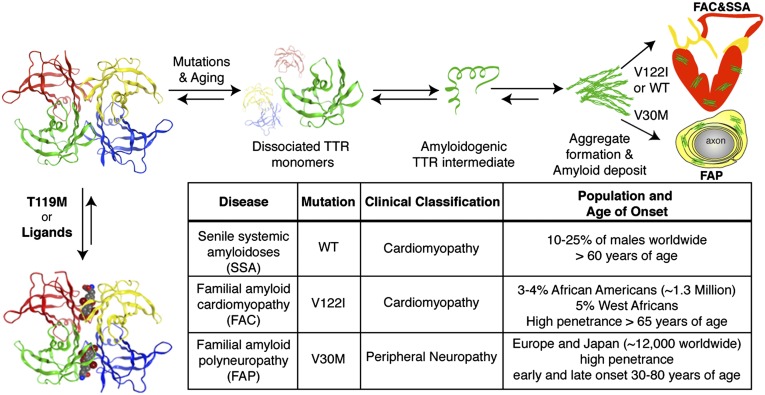
Fig. 1.
The TTR amyloidogenesis cascade and a table summarizing TTR-mediated amyloidoses. TTR amyloidoses require rate-limiting tetramer dissociation to dimers, followed by dissociation into monomers before partial unfolding of monomers yields the aggregation-prone amyloidogenic intermediate. The amyloidogenic intermediate can misassemble to form a variety of toxic aggregates, including amyloid fibrils. Disease-associated destabilizing mutations can kinetically or thermodynamically destabilize TTR. Kinetic stabilization can be achieved through trans allelic suppression with the kinetically stabilized T119M-TTR, binding to T4 or other small molecules (Lower Left).