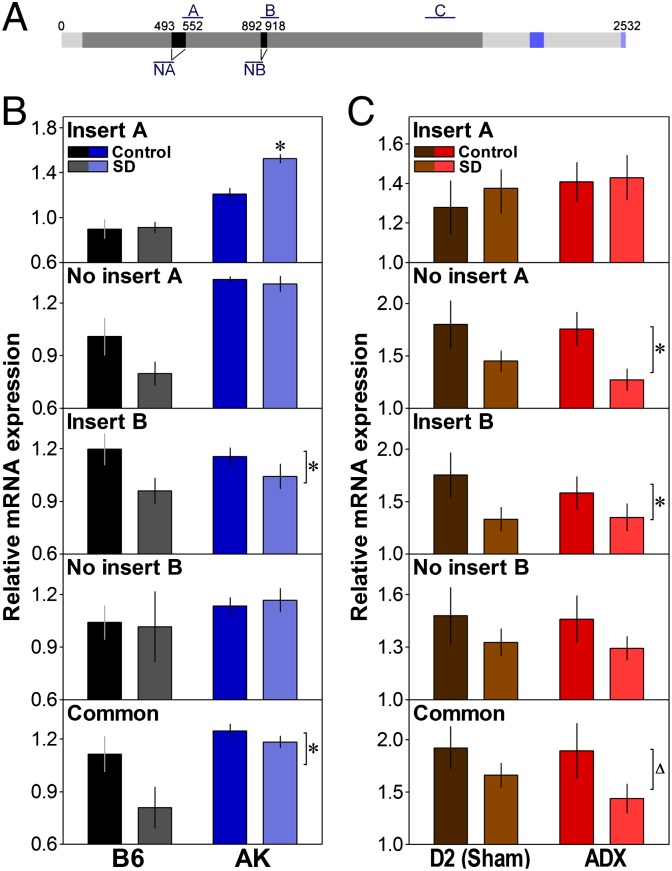
Fig. 1.
Effect of SD on the expression of Nlg1 transcript variants. (A) Scheme of the Nlg1 mRNA showing position of splice sites and qPCR amplicons (A and NA or B and NB, with and without insert A or B, respectively; C, common probe). Dark gray, cholinesterase domain (94–1,878 bp); blue, transmembrane domain (2,086–2,142 bp); light blue, PSD95-binding domain (2,512–2,529 bp). (B) Relative expression of Nlg1 transcripts in the forebrain of C57BL/6J (B6) and AKR/J (AK) mice at ZT6 (6 h after light onset) under the control condition (n = 4 for B6 and AK) or after a 6-h SD (n = 3 for B6, 4 for AK). SD significantly decreased the expression of Nlg1 with insert B and common Nlg1 (condition effects: F1,12 ≥ 5.1, *P < 0.05) and increased the expression of Nlg1 with A only in AK mice (interaction: F1,12 = 6.8, *P < 0.05: compared with Control). AK mice also expressed more common Nlg1 and Nlg1 without A and without B than B6 mice (strain effects: F1,12 ≥ 9.8, P < 0.01). (C) Expression of Nlg1 transcripts in the forebrain of DBA/2J (D2) mice at ZT6 under the control condition or after a 6-h SD in mice submitted to either a sham surgery (n = 7/group) or an ADX (n = 6/group). SD decreased the expression of Nlg1 without A and with B (condition effects: F1,22 ≥ 4.2, *P ≤ 0.05), and a similar tendency was found for common Nlg1 (F1,22 = 3.7, ∆P < 0.07).