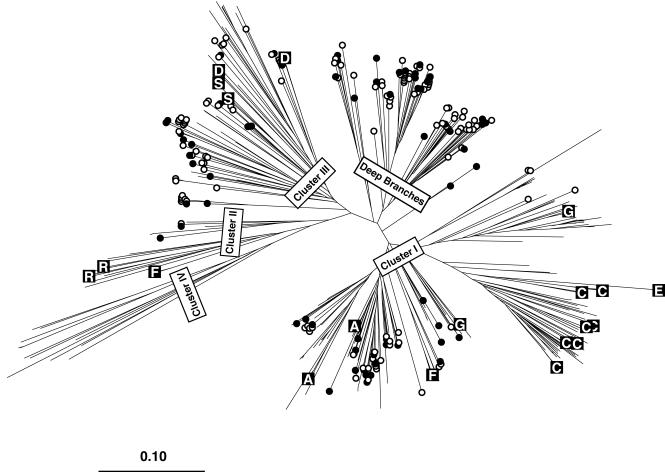
FIG. 1.
Neighbor-joining tree constructed from an uncorrected distance matrix among 447 nifH sequence fragments generated as part of this study (228 fragments) or retrieved from GenBank (219 fragments). For GenBank sequences, only those sequences from cultivated bacteria that spanned at least the region corresponding to our fragment were included. Sequences belonging to commonly recognized major clusters (clusters I to IV [5]) and some additional deep branches are labeled. Branches with open or closed circles contain sequences derived from Chesapeake Bay samples. Closed circles indicate those clones represented as probes on the array. Branches marked with a letter in a black box are sequences obtained from cultivated bacteria as part of this study that are also represented as probes on the array. The boxed letters indicate the phylogenetic designation of the bacterium from which the sequence was derived (A, D, E, and G indicate members of the alpha, delta, epsilon, and gamma subdivisions of the Proteobacteria, respectively; C, cyanobacteria; F, Firmicutes; S, green sulfur bacteria, R, Archaea).