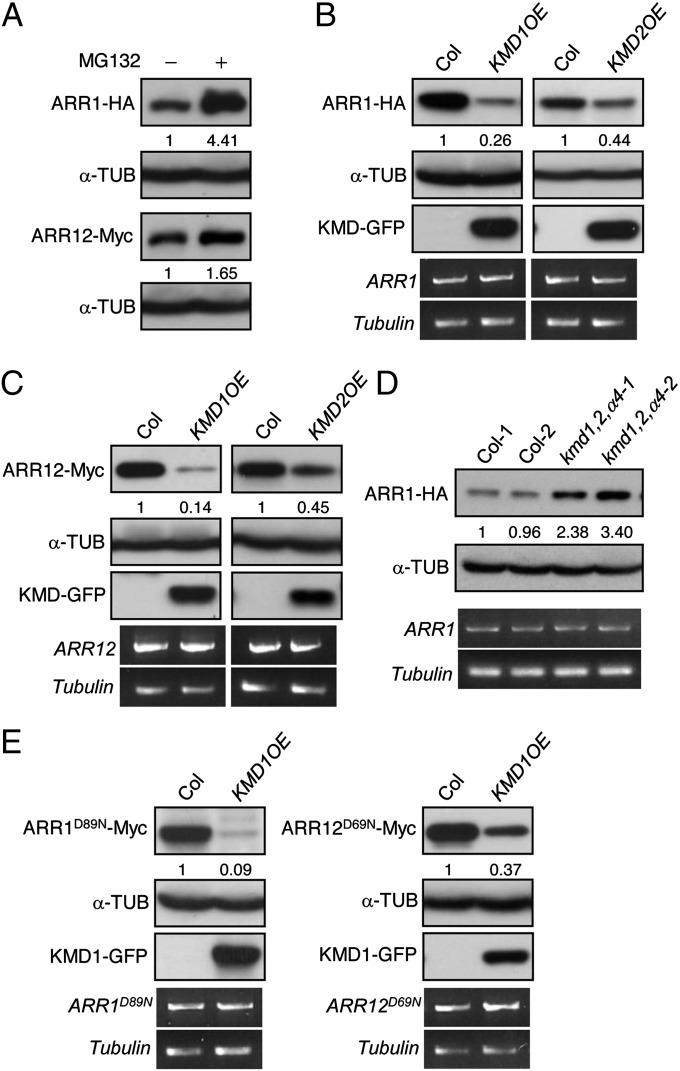
Fig. 4.
KMD1 and KMD2 target type-B ARR proteins for degradation. (A) Proteasome-dependent degradation of ARR1 and ARR12. Mesophyll protoplasts from 35S::ARR1-HA or 35S::ARR12-Myc lines were incubated for 3 h in the presence or absence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 and protein extracts analyzed by immunoblotting. α-Tubulin served as a loading control. (B and C) Overexpression of KMD1 and KMD2 results in reduced protein levels of ARR1 (B) and ARR12 (C). Protein levels of the tagged proteins were determined by immunoblot analysis using anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies, with α-tubulin as the loading control. Transcript levels for transgenes were detected using HA- or Myc-tag–specific primers by RT-PCR, with β-tubulin as the loading control. (D) Decreased expression of the KMD family results in increased protein levels of ARR1. Immunoblot detection of ARR1-HA in 10-d-old wild-type and kmd1,2,α4 seedlings, with α-tubulin as the loading control is shown. Each lane represents a protein sample from independent seedlings. (E) Degradation of ARR1 and ARR12 is not dependent on the conserved phosphorylation target Asp. The predicted phosphorylation target residues on ARR1 and ARR12 were mutated to Asn (ARR1D89N; ARR12D69N), and stability was examined in the presence or absence of KMD1 overexpression.