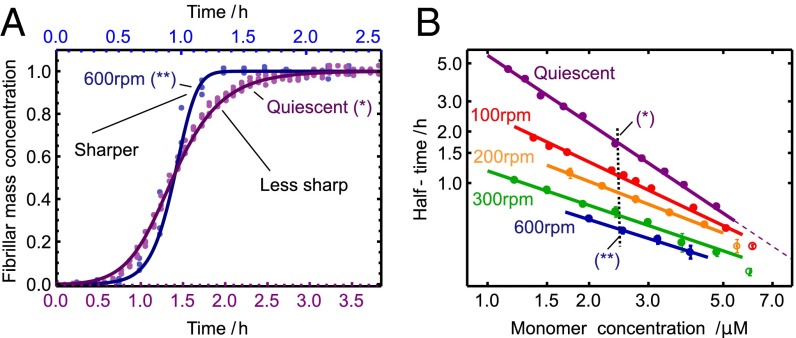
Fig. 3.
Shear alters the symmetry of the reaction profile. (A) Comparison of the shape of the kinetic profiles under quiescent and high-shear conditions (33), corresponding to concentrations marked B with a vertical dotted line. The solid lines are the theoretical rate laws with the rate constants identified in Fig. 2. (B) Power-law relationship for the monomer dependence at varying shear rates from Fig. 2 A–E (Lower). The weakening of the monomer dependence, given by the magnitude of the slope, occurs as fragmentation is gradually introduced as a molecular mechanism. Predicted deviations from the power law at high concentration are shown as open circles (SI Text).