Fig. 2.
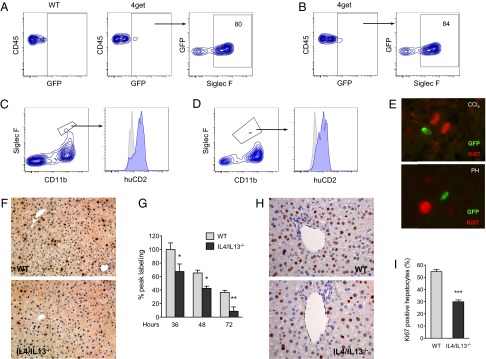
IL-4/IL-13 promote liver regeneration. (A and B) Identification of eosinophils as the major cell population competent for IL-4 secretion after CCl4-mediated injury (A) and PH (B). Two days after administration of CCl4 or PH in the IL-4 reporter mice (4get mice), the nonhepatocyte fraction was isolated and analyzed for expression of GFP and markers of eosinophils. Representative data from 3 independent experiments are shown in A and B. (C and D) Eosinophils produce IL-4 in injured livers. Expression of huCD2 on eosinophils (Siglec F+CD11b+) 2 d after PH (C) or CCl4-induced injury (D) in KN2 mice. Isotype, gray histogram; huCD2, blue histogram. (E) GFP+ cells localize in proximity to proliferating hepatocytes (Ki67+) 2 d after injury with CCl4 (Upper) or PH (Lower). (F) Liver sections stained for BrdU 36 h after partial hepatectomy. Representative images of WT and IL-4/IL-13−/− are shown. (G) Liver regeneration in WT and IL-4/IL-13−/− mice was assessed by BrdU incorporation at indicated times after PH (n = 4–9 mice per genotype per time). (H) Representative liver sections from WT and IL-4/IL-13−/− mice were stained for Ki67 2 d after administration of CCl4. (I) Percentage of Ki67+ hepatocytes in WT and IL-4/IL-13−/− mice 2 d after CCl4 treatment (n = 5 mice per genotype). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
