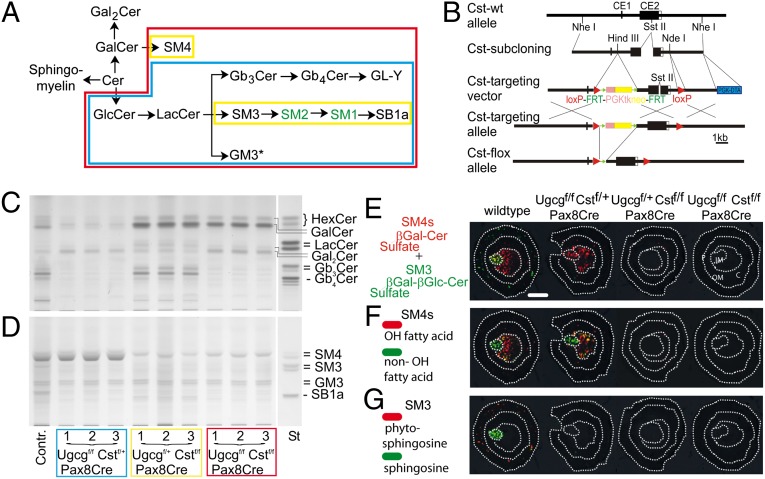
Fig. 1.
Pax8-driven deletion of renal neutral and sulfated GSLs. (A) Ugcg- and Cst-dependent synthesis of neutral and acidic GSLs in the mouse kidney. (B) Cloning strategy for the disruption of the Cst gene. Disruption of the Ugcg gene has been described previously (47). (C and D) Neutral (C) and acidic (D) GSL extracts from one control mouse and Ugcgf/f , Cstf/f, and Ugcgf/f Cstf/f Pax8Cre mice (n = 3 each) were separated by TLC. Aliquots from extracts corresponding to 4 mg of dry weight of kidneys were loaded. Pronounced reduction of both GlcCer-based and all sulfated GSLs (SM4s, SM3, and SB1a) was found in kidneys from Ugcgf/f Cstf/f Pax8Cre mice only. *GM3 ganglioside is obviously expressed in other cell types (endothelial, stromal) than those that express the Pax8Cre recombinase and remains therefore unaltered in mutant kidney (A and D). (E–G) MALDI-MSI of renal sulfatides in control mice and mice with kidney-specific sulfatide deficiency. (E) The sum of all detected isoforms of SM4s (red) and complex SM3 (green) that overlap in the papilla. (F) SM4s isoforms with hydroxylation in the fatty acid (red) are mainly detected in the inner medulla, whereas more lipophilic isoforms without this modification (green) are mainly detected in the papillary region. (G) Complex SM3 without any modification in the ceramide anchor (green) shows a specific location to the papilla, whereas more hydrophilic isoforms with a hydration of the double bond of the sphingoid base (red) are located to the renal cortex. (Scale bar, 1 mm.) C, cortex; IM, inner medulla; OM, outer medulla; P, papilla. Each section shown is representative of n = 3 mice per genotype.