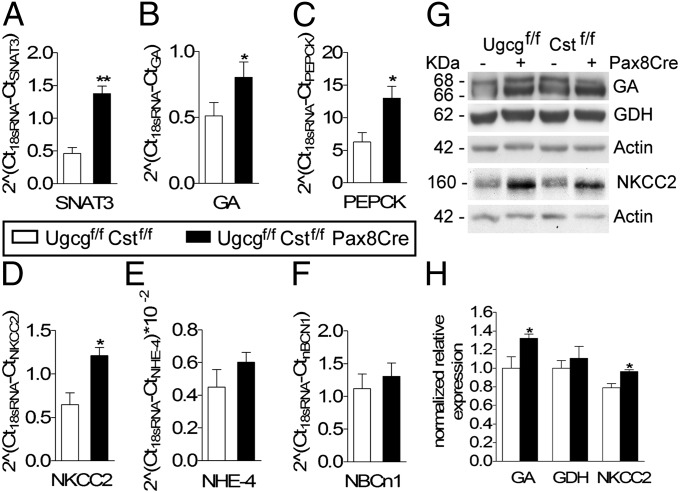
Fig. 5.
Expression of enzymes and transporters relevant for ammonium production, TAL reabsorption, and delivery to the medullary interstitium. (A–F) Total mRNA was isolated from kidneys of 9-d acid-loaded control and renal Ugcg/Cst-deficient mice (n = 5 or 6 per genotype) and analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (A) The sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter (SNAT3) and (B) the mitochondrial glutaminase (GA) involved in production of NH4+, as well as (C) the cytoplasmic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) mediating the generation of HCO3− and (D) the apical Na+-K+/NH4+-2Cl− cotransporter 2 (NKCC2) mediating net NH4+ reabsorption in the TAL were significantly increased in renal Ugcg/Cst-deficient kidneys. (E) The basolateral Na+/NH4+-H+ exchanger 4 (NHE-4) and (F) the electroneutral Na+-bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCn1) were elevated too, however not significantly. Means ± SEM are shown (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (G and H) Western blot analysis of mitochondrial glutaminase (GA) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), both involved in the production of NH4+, as well as the NKCC2 cotransporter in chronic acid-loaded mice. The cytoplasmic and membrane protein samples shown are representative of n = 3 in controls and n = 5 in mutant mice. Intensities of bands were densitometrically evaluated. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05).