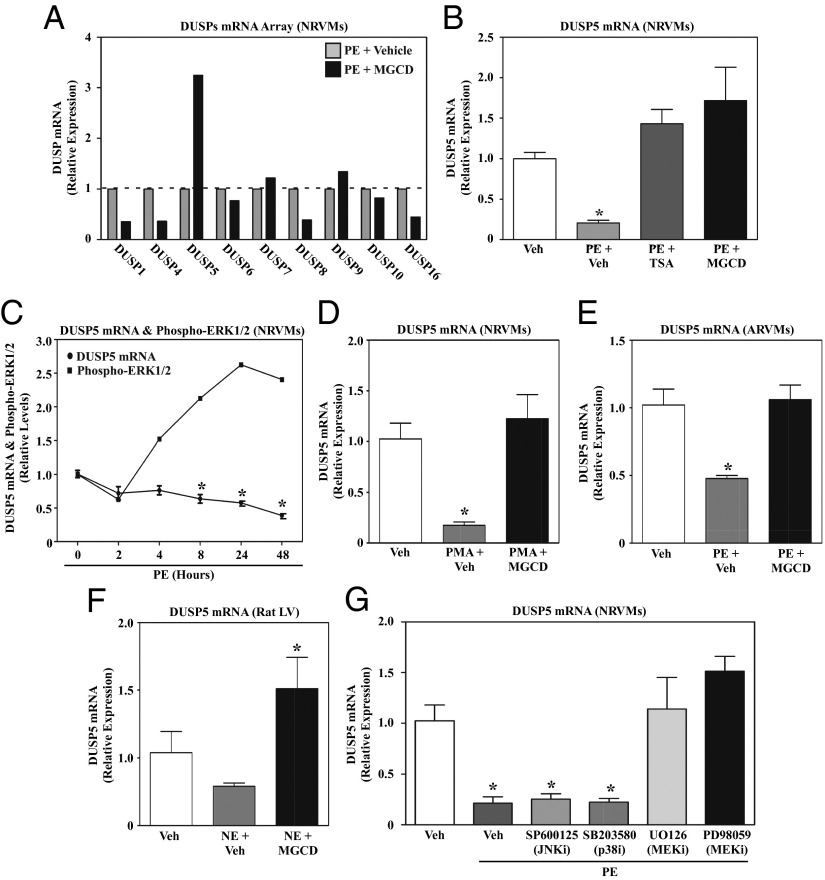
Fig. 3.
Signal-dependent repression of DUSP5 expression in cardiomyocytes requires class I HDAC and MEK catalytic activity. (A) NRVMs were stimulated with PE for 48 h in the absence or presence of MGCD0103 or DMSO vehicle control. RNA was harvested and expression of the indicated MAPK-specific dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) was quantified using a PCR array. (B) NRVMs were left untreated or treated with PE for 48 h in the absence or presence of TSA or MGCD0103. DUSP5 mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR. (C) NRVMs were stimulated with PE and harvested over time for analysis of DUSP5 mRNA expression and phospho-ERK1/2 levels. Densitometry was used to quantify phospho-ERK normalized to total ERK. (D) NRVMs were left untreated or stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) for 48 h in the absence or presence of MGCD0103, and DUSP5 mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR. (E) Adult rat ventricular myocytes (ARVMs) were treated for 48 h with PE in the absence or presence of MGCD0103, and DUSP5 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR. (F) Adult rats were administered MGCD0103 (10 mg/kg) or vehicle control by i.p. injection for 3 d and were subsequently given a single i.p. injection of norepinephrine (NE). Animals were killed 2 h post-NE injection and DUSP5 mRNA expression in the LV was analyzed by qPCR. n = 3 animals per condition; *P < 0.05 vs. unstimulated, vehicle-treated rats. (G) NRVMs were left untreated or stimulated with PE for 48 h in the absence or presence of a JNK inhibitor (SP600125), a p38 inhibitor (SB203850), or two different MEK inhibitors (U0126 and PD98059). DUSP5 mRNA expression was assessed by qPCR. For qPCR analysis in B–E and G, three plates of cells were used per condition; *P < 0.05 vs. unstimulated, vehicle-treated cells.