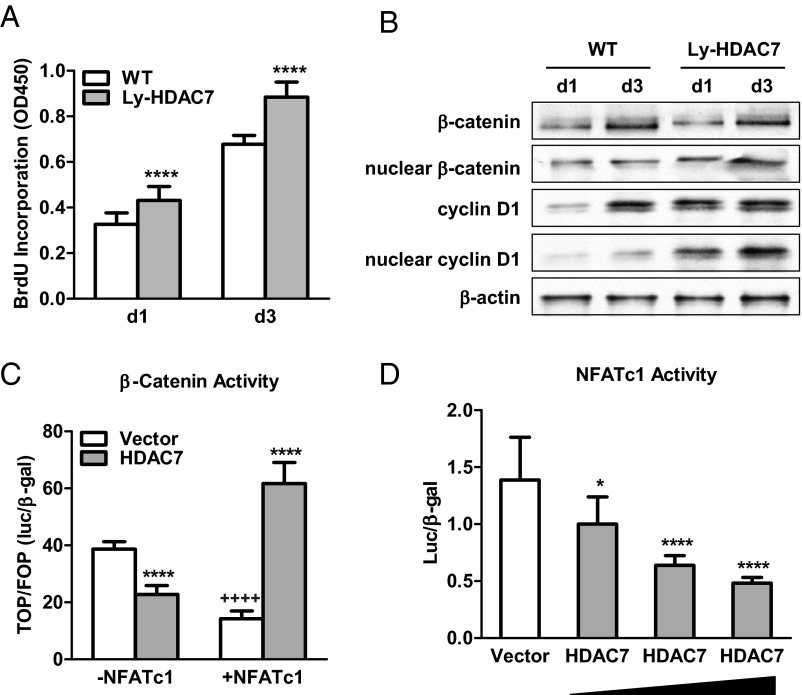
Fig. 4.
HDAC7 Reverses RANKL-mediated β-catenin switch by suppressing NFATc1. A, Osteoclast precursor proliferation was increased by HDAC7 deletion (n = 10). BrdU incorporation was compared between bone marrow cultures from Ly-HDAC7 knockout mice or littermate controls 1 or 3 d after MCSF treatment. B, β-Catenin and cyclin D1 protein levels during precursor proliferation were elevated by HDAC7 deletion. Whole-cell extract or nuclear extract was isolated from the bone marrow cultures 1 or 3 d after MCSF treatment, and immunoblotted with antibodies for β-catenin, cyclin D1, or β-actin. C, β-Catenin activity was inhibited by HDAC7 in the absence of NFATc1, but stimulated by HDAC7 in the presence of NFATc1 in a transient transfection assay. TOP-flash activity was normalized by FOP-flash activity control (n = 6). *, HDAC7 compared with vector control; +, −NFATc1 compared with +NFATc1. D, NFATc1 activity was suppressed in a dose-dependent manner by HDAC7 in a transient transfection assay (n = 6). Statistical analyses were performed with Student's t test and are shown as mean ± sd; *, P < 0.05; **** or ++++, P < 0.001. WT, Wild type.